As the global community grapples with the implications of climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, the race for innovative, sustainable energy alternatives has become crucial. Among the various avenues being explored, hydrogen has emerged as a leading candidate for a clean energy future. However, this promise is shadowed by significant logistical challenges surrounding hydrogen’s storage and transport. Hydrogen gas, in its essence, is an inefficient energy carrier due to its volatility and the complexities involved in its safe handling.
In an exciting turn of events, researchers from the Tokyo Institute of Technology and the Tokyo University of Science have boldly ventured into a solution that transcends the hurdles of hydrogen use—ammonia (NH3). As a cleaner and more manageable energy carrier, ammonia presents itself not just as a substitute for hydrogen, but as a potential cornerstone for the future of sustainable energy.
The Breakthrough of Novel Compounds
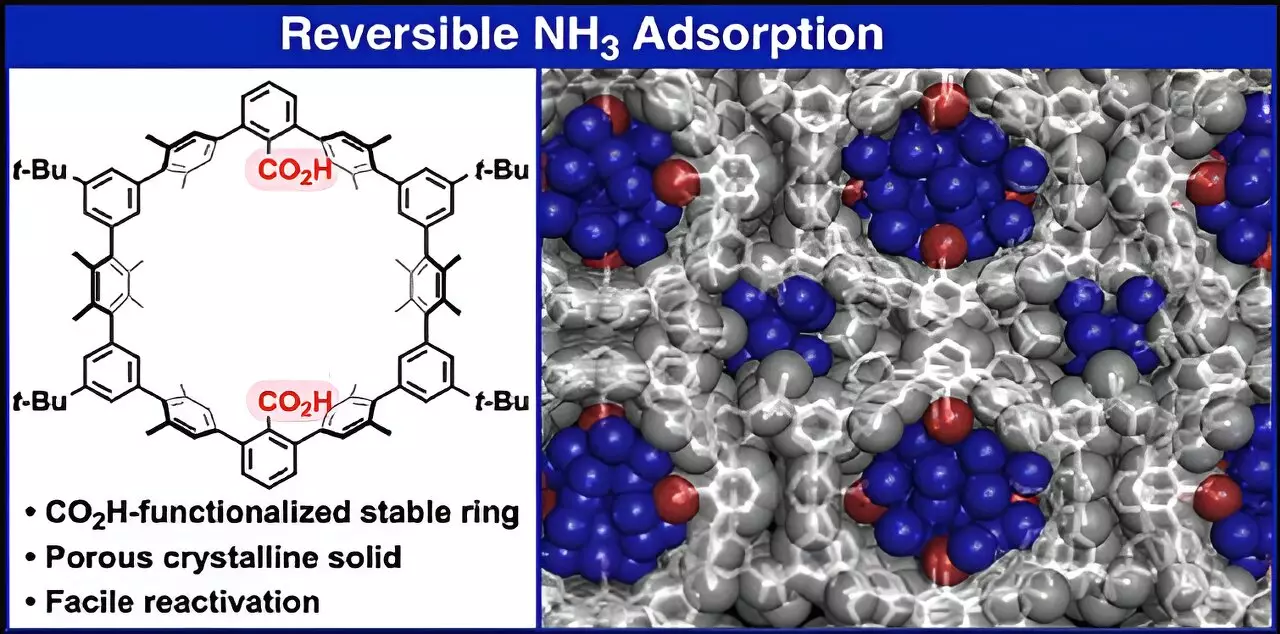
Under the guidance of Associate Professor Kosuke Ono, the team has pioneered the development of a groundbreaking material known as 1a. This compound functions by efficiently adsorbing ammonia at high densities, providing a practical method for its recovery. The significance of this innovation lies not only in the high efficiency of the material but also in the chemical stability and ease of releasing ammonia when conditions are favorable.
The crux of this research hinges upon the unique structural design of crystalline solid 1a (N), formed by cyclic oligophenylenes. These compounds possess acidic CO2H functional groups within their ring structure, leading to the formation of parallel nanochannels that facilitate effective ammonia absorption. This process allows the 1a material to achieve an impressive packing density of ammonia at room temperature, closely rivaling that of liquid ammonia.
The Benefits of Ammonia Over Hydrogen
One of the most staggering advantages of using ammonia as an energy carrier is its inherent safety and logistical viability. Unlike hydrogen, which requires elaborate cold storage or intricate pressurization techniques, ammonia can be handled with much simpler infrastructure. This not only drastically reduces operating costs but also allows for a swift transition from existing ammonia production facilities to new energy applications.
Moreover, when combusted, ammonia produces nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O), thus avoiding harmful carbon emissions—making it an extraordinarily attractive option in the fight against climate change. Professor Ono aptly summarizes this perspective, emphasizing that ammonia encapsulates the dual role of being a hydrogen source while concurrently standing as a carbon-free energy carrier.
The Future of Ammonia Storage Technologies
The potential of ammonia does not solely rest with its combustion properties; it extends into various applications through the innovative compound 1a (N). One of the most commendable features of this novel material is its ability to release absorbed ammonia merely by adjusting surrounding pressure, a significant step forward in addressing the challenges posed by conventional ammonia storage materials. Traditionally, these materials struggled with residual ammonia during desorption, significantly limiting their efficiency; however, 1a (N) elegantly circumvents this issue.
Beyond its current applications, there exists a realm of exploration with the chemical modification of 1a. By substituting the CO2H groups with different functional groups, researchers could potentially address storage challenges for other reactive gases, such as HCl or Cl2, broadening the horizon for diverse applications in chemical processing and industrial operations.
As we stand at the crossroads of a global energy transition, the developments concerning ammonia as an energy carrier and the innovative compound 1a pave the way for a more sustainable future. The research team at Tokyo Institute of Technology and Tokyo University of Science illuminates a path that not only addresses current energy dilemmas but also heralds the dawn of a new era in clean energy solutions. With continued exploration and dedication, the promise of ammonia shines brightly, intertwining science and sustainability for a better tomorrow.

Leave a Reply