Northern Europe benefits from a relatively warm climate compared to other regions at similar latitudes, such as major Canadian cities. This warmth is attributed to a major ocean current, the Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current (AMOC), which carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to the north Atlantic, providing heat that keeps northern European ports ice-free. However, the future of this crucial current is uncertain due to the impacts of global warming.
New Findings on the Future of the AMOC
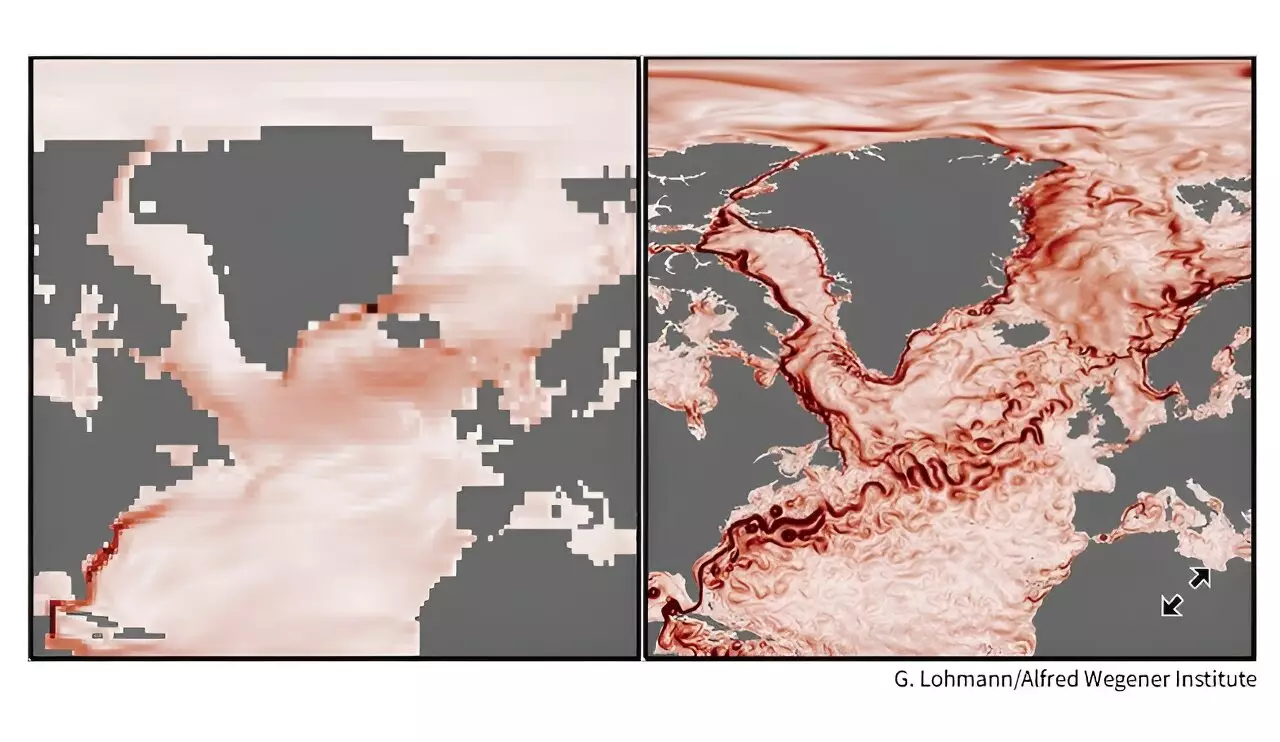
Recent studies utilizing high-resolution climate models have uncovered surprising revelations about the potential fate of the AMOC. Contrary to previous beliefs that the AMOC would uniformly weaken, the new models suggest that the current could experience abrupt collapses in some regions and unexpected strengthening in others. These findings challenge traditional climate change projections and highlight the complexity of ocean current dynamics.
One of the key insights from the high-resolution climate models is the identification of tipping points within the AMOC system. Tipping points are thresholds at which small changes can lead to drastic shifts in the state of a system. In the case of the AMOC, localized shifts and regional variations were observed, indicating the presence of tipping points that were previously unknown. These discoveries emphasize the need to incorporate regional dynamics into future AMOC forecasts to better understand the potential impacts on climate and marine ecosystems.
The Role of Climate Models in Anticipating Change
The use of advanced climate models, such as the Community Earth System Model, has provided a more detailed view of the AMOC and its potential future trajectories. By simulating different scenarios, including extreme greenhouse gas emissions, researchers have been able to predict changes in the AMOC’s activity over the coming century. These models underscore the critical importance of advancing climate modeling techniques to accurately anticipate and respond to the evolving dynamics of our planet’s systems.
As global temperatures continue to rise and the impacts of climate change become more pronounced, the future of ocean currents like the AMOC remains uncertain. The findings from recent studies highlight the need for proactive measures to mitigate the effects of climate change and prevent irreversible damage to crucial components of the Earth’s climate system. By incorporating regional dynamics and tipping points into climate models, scientists can better prepare for potential changes and help inform policy decisions aimed at preserving the stability of our planet.
The fate of the Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current is a complex and uncertain issue that requires careful monitoring and analysis. Through the use of advanced climate models and a deeper understanding of ocean current dynamics, scientists can gain valuable insights into the potential future of the AMOC and its implications for global climate systems. As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, it is essential to prioritize research and innovation in order to protect the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.

Leave a Reply