Recent research conducted by ETH Zurich has shed light on the significant impact that climate change and global warming have on Earth’s polar motion. Through the use of AI methods, researchers have been able to unravel the complex causes of long-term polar motion and its implications on the Earth’s rotation.
Climate Change and Earth’s Rotation
The melting of ice masses in Greenland and Antarctica due to climate change is resulting in a shift of mass on the Earth’s surface. This shift in mass is leading to changes in the Earth’s rotational speed, affecting the length of the day on Earth. Researchers explain this phenomenon by likening it to a figure skater performing a pirouette, where the masses moving away from the axis of rotation increase physical inertia, slowing down the Earth’s rotation.
Findings of the Research
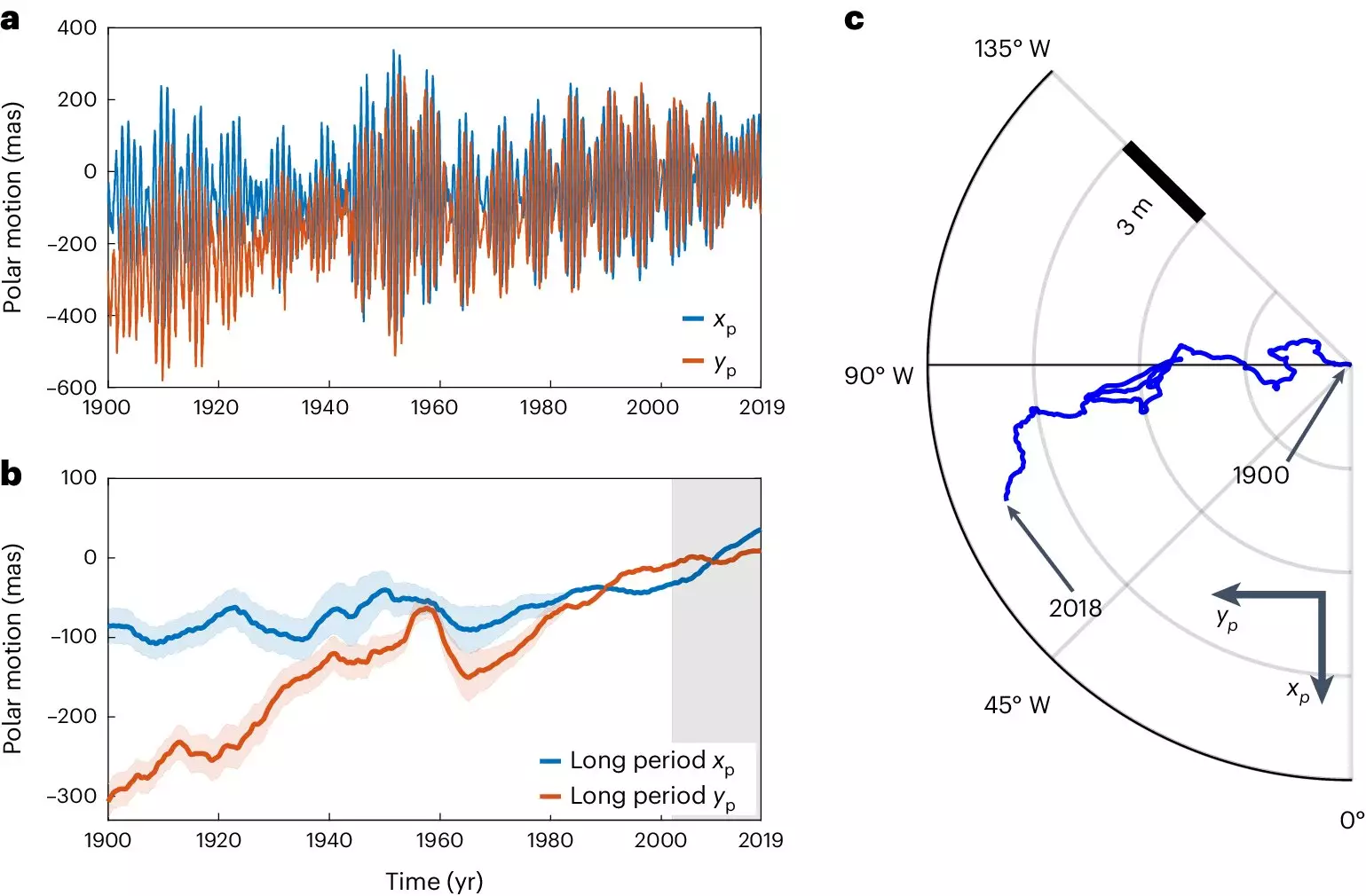
The studies published by the ETH Zurich researchers indicate that climate change is not only increasing the length of the day by a few milliseconds but also altering the Earth’s axis of rotation. The movement of water from the poles to lower latitudes is slowing down the speed of rotation, in addition to tidal friction triggered by the moon. Surprisingly, the research concludes that human-induced global warming may have a more significant impact on the Earth’s rotational speed than the effect of the moon.
The researchers have discovered that the processes occurring on the Earth’s surface, in its mantle, and in its core are interconnected and influence each other. Climate change is not only causing shifts in the Earth’s axis of rotation but also potentially impacting processes deep inside the Earth. The findings suggest that ongoing climate change could have a greater reach than previously assumed, affecting even the dynamics of the Earth’s core.
Technological Advancements
The researchers utilized physics-informed neural networks, a novel AI method, to model the effects on the Earth’s surface, mantle, and core. These algorithms have allowed for a comprehensive understanding of the causes of long-term polar motion and have enabled the accurate prediction of the Earth’s rotational poles’ movements since 1900.
While the effects of climate change on Earth’s polar motion are considered minor and unlikely to pose a risk, they have implications for space navigation. Even subtle changes in the Earth’s rotation can have significant consequences when navigating in space, emphasizing the importance of understanding and accounting for these effects when conducting space missions.
The research conducted by ETH Zurich highlights the intricate relationship between climate change and Earth’s polar motion. By leveraging AI methods and advanced modeling techniques, researchers have been able to unravel the underlying causes of long-term polar motion and its implications for the Earth’s rotation. This groundbreaking research opens up new avenues for understanding the Earth’s dynamic systems and underscores the need for proactive measures to address the impacts of climate change on our planet.

Leave a Reply