Climate change is a pressing issue that is affecting our planet in various ways. Recent research has shown that the impacts of climate change are not uniform across different regions, with temperature rising differently based on factors such as latitude and elevation. This variability in Earth’s climate patterns is known as climate heterogeneity, and it plays a crucial role in shaping the future of our planet.
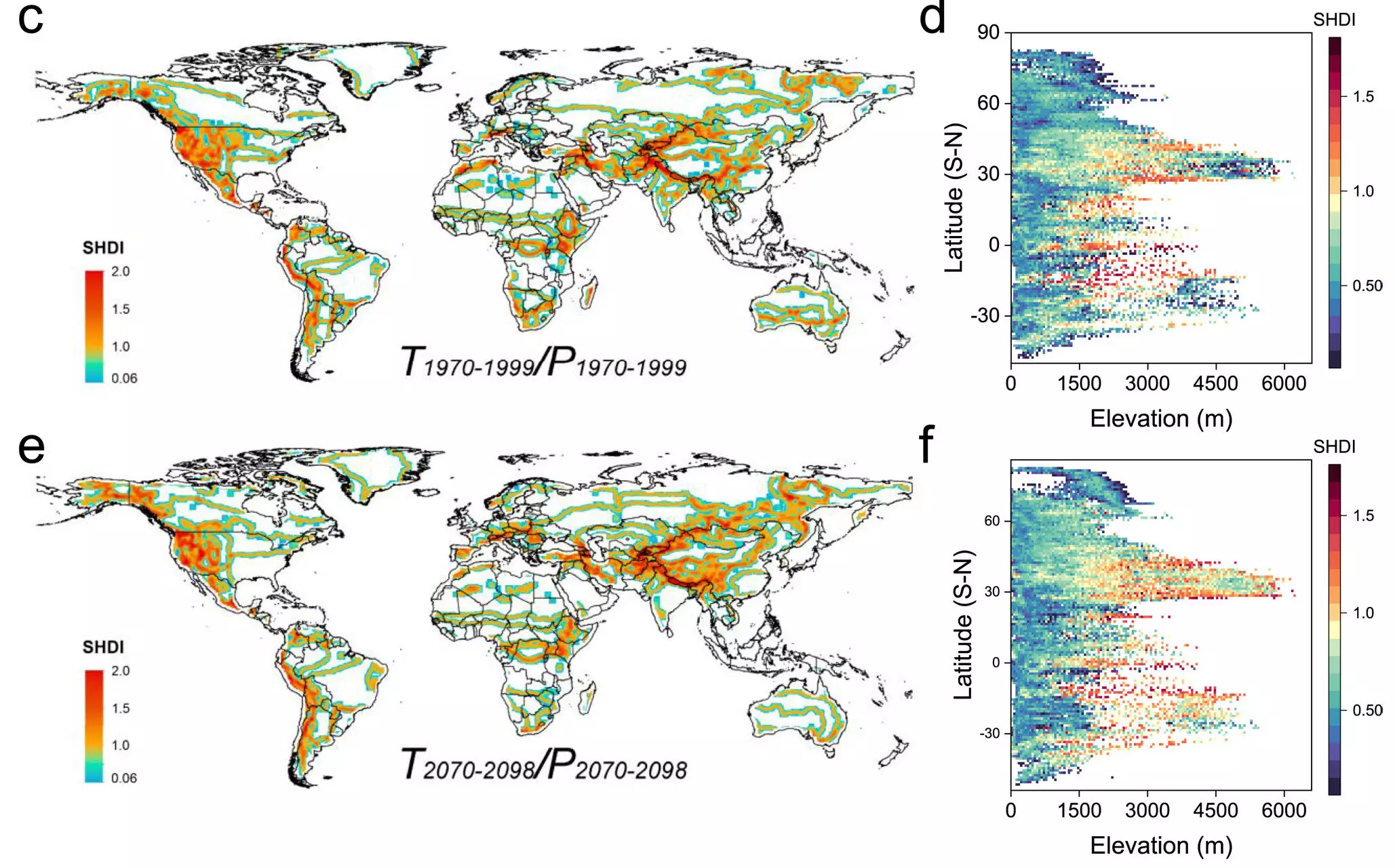
An in-depth study conducted by Yanlong Guan and his colleagues from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, China, focused on understanding the role of elevation in climate heterogeneity. By analyzing changes in organismal diversity using Shannon’s diversity index and the Köppen-Geiger climate classification, the researchers were able to gain insights into how elevation impacts climate patterns.
The research team found that at lower elevations (less than 2,000 m), where temperatures rise rapidly, there is a reduction in Shannon’s diversity index. This leads to the proliferation of similar arid and tropical conditions over a large area. In contrast, at higher elevations (more than 2,000 m), there is greater climate heterogeneity, with the diversity index continuing to increase as environmental conditions slowly warm. This creates small patches of cold climates at the highest elevations.
The research team used climate simulations to understand the driving forces behind these patterns. The simulations revealed that anthropogenic climate change is the primary driver of the distinct shift in climate heterogeneity between lower and higher altitudes. As a result of this shift, certain regions, such as North America, may experience reduced climate variability, while high elevation areas like the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau could act as cold refugia.
The projections from this research suggest that up to 46% of land surfaces may transition to warmer and drier conditions by the end of the century. This homogenization of climate types could pose a threat to habitat and species distributions. However, understanding the climate variability that persists at higher elevations could be crucial in ensuring the survival of human, animal, and plant communities in the face of rising temperatures and the associated social, economic, and environmental challenges.
The study of climate heterogeneity sheds light on the complex interactions between elevation, temperature, and precipitation in shaping Earth’s climate patterns. As we continue to grapple with the effects of climate change, it is crucial to consider the role of elevation in understanding and mitigating these impacts. By recognizing the potential of higher elevations as refugia for diverse ecosystems, we can better prepare for the challenges that lie ahead in an uncertain climate future.

Leave a Reply