Access to clean and safe water is a fundamental necessity for human survival. Unfortunately, clean water is a limited resource, and many regions around the world face water scarcity. The availability of water depends largely on local bodies of water, making arid regions particularly vulnerable to water shortages. However, even in dry areas, there is a certain amount of water vapor present in the air, offering a potential source of moisture that can be harvested.
Recently, researchers have developed a groundbreaking device designed to capture humidity from the air and generate potable water. This compact device features absorbent-coated fins that are designed to trap moisture and release it as clean water when heated. The innovative design of this device has the potential to address the growing demands for water, especially in arid locations where access to clean water is limited.
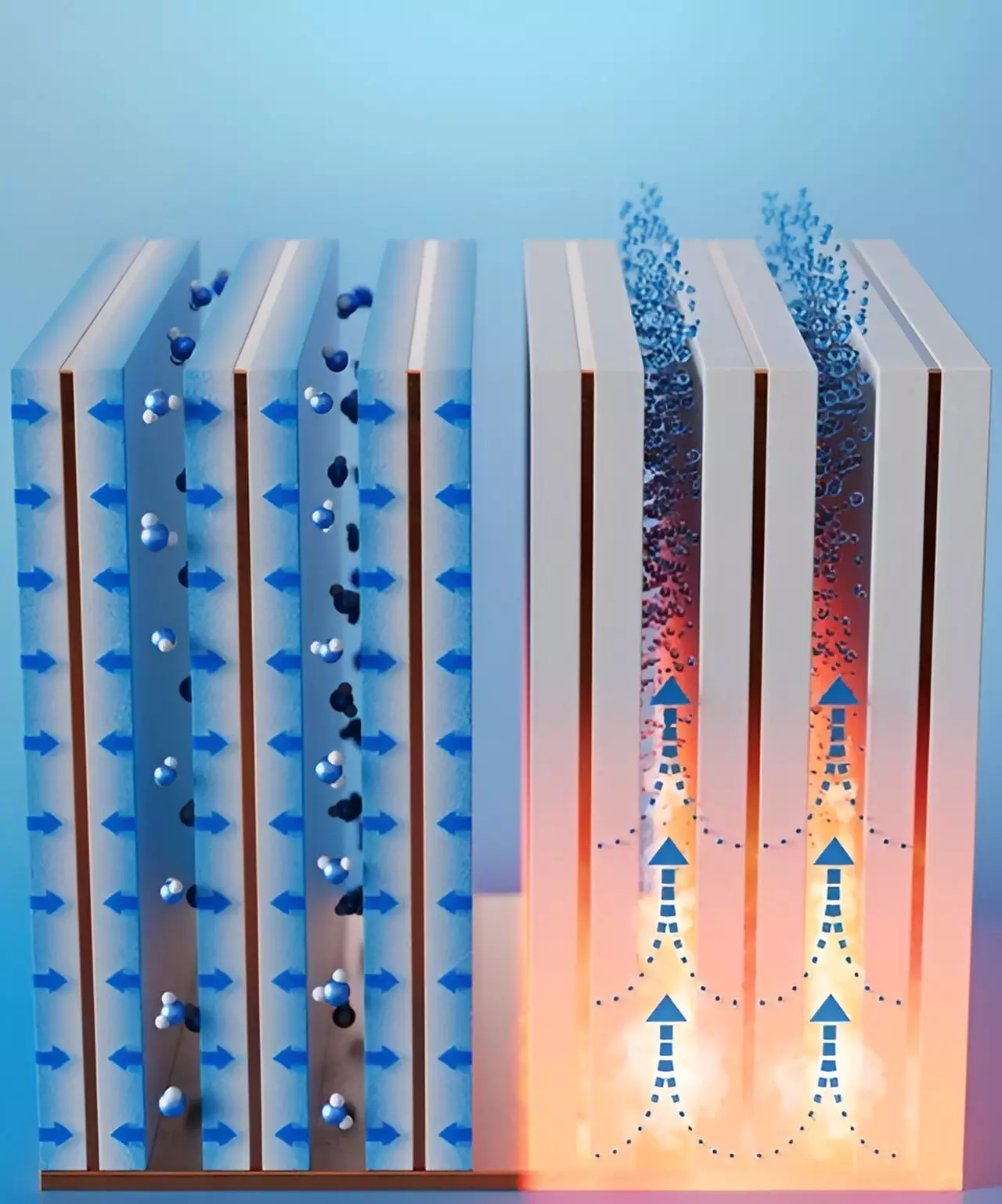
The device works by utilizing special materials like zeolites, metal-organic frameworks, or temperature-responsive hydrogels to extract moisture from the air. These absorbent materials are incorporated into the design of the device, which consists of water-adsorbent “fins” that are coated with a commercially available zeolite. Unlike previous systems that focused solely on material development, this device combines material properties with the design of the adsorption bed to create a more efficient and compact water harvesting solution.
Proof-of-Concept Demonstration
In a proof-of-concept demonstration, the researchers tested the device in air with 10% relative humidity, simulating desert-like conditions. The results were impressive, with the fins saturating within an hour and releasing the trapped moisture when the base reached a temperature of 363 Fahrenheit. Based on their calculations, the researchers estimate that 1 liter of absorbent coating on the fins could produce up to 1.3 liters of potable water per day in air with 30% relative humidity. This volume is two to five times greater than what was previously achieved with similar devices.
The development of this device represents a significant advancement in water harvesting technology. With further research and development, this system could potentially be integrated into existing infrastructures that produce waste heat, such as buildings or transportation vehicles. This integration could provide a cost-effective and sustainable solution for generating potable water in arid regions, where water scarcity is a pressing issue. The potential for rapid moisture capture and water harvesting multiple times per day makes this device a promising solution for addressing water scarcity challenges worldwide.
The innovative water harvesting device developed by Xiangyu Li, Bachir El Fil, and their colleagues offers a glimpse into the future of water sustainability. By harnessing the power of humidity in the air, this device has the potential to provide clean and safe water to populations in need, particularly in arid regions where access to water is limited. The implications of this breakthrough in water harvesting technology are far-reaching, offering hope for a more sustainable future where clean water is a accessible resource for all.

Leave a Reply