In recent years, the field of chemistry has been revolutionized by the collaboration between chemists and computer scientists to create AI applications that assist in various aspects of chemical research. The traditional methods of trial and error in chemistry have paved the way for innovative technologies that streamline processes and enhance accuracy in predicting small molecule structures.
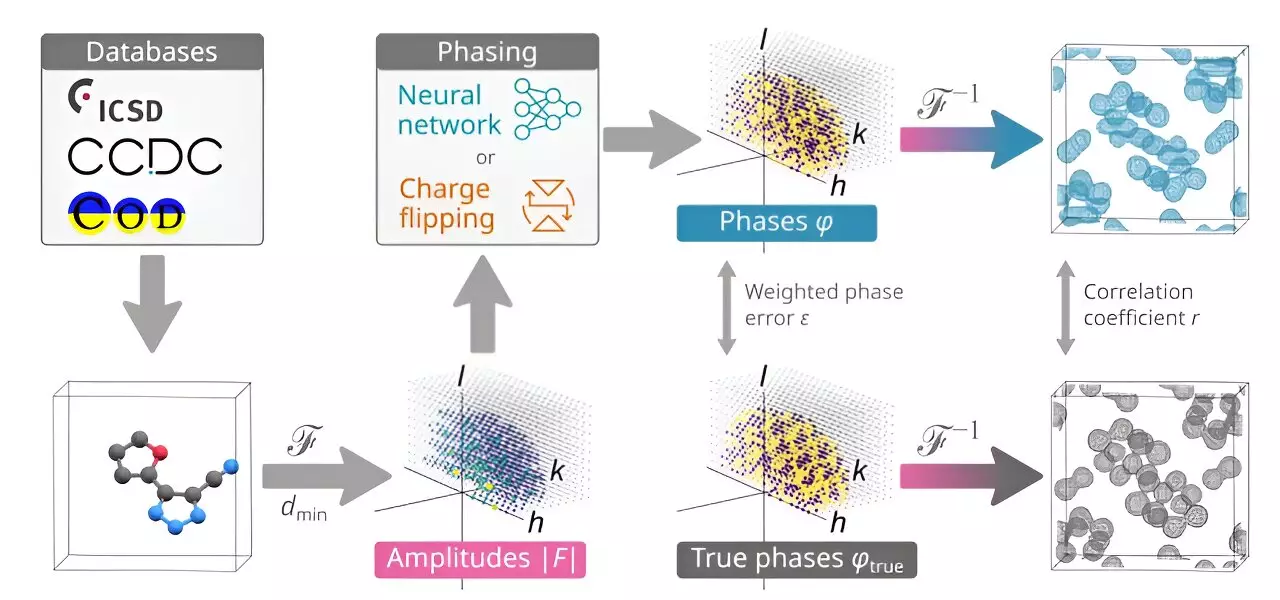
A groundbreaking study conducted by a team of chemists at the University of Copenhagen introduced an AI application named PhAI, designed to determine the phase of x-rays diffracted by crystals to predict the structure of small molecules. This innovative approach represents a significant advancement in the field of chemistry, shedding light on a previously challenging aspect of crystallography.
The conventional process of predicting the structure of small molecules involves converting them into solid crystals and analyzing the diffraction patterns produced by x-ray beams. While measuring the intensity of x-rays is feasible, determining their phase presents a formidable challenge for researchers. The ambiguity in phase measurement often results in blurry diffraction patterns, making it difficult to accurately deduce the molecular structure.
The research team utilized AI technology to address the limitations of phase estimation in crystallography. By developing a sophisticated AI model trained on millions of simulated small molecule structures and their corresponding fuzzy diffraction patterns, the researchers were able to establish a reliable correlation between crystal structures and diffraction patterns.
The successful testing of the PhAI application demonstrated its exceptional accuracy in predicting the structure of 2,400 small molecules with known structures. This remarkable achievement signifies a significant milestone in the field of chemistry, showcasing the potential for AI to enhance the efficiency and precision of chemical research endeavors.
Moving forward, the research team aims to expand the capabilities of PhAI to accommodate larger molecules beyond 50 atoms. By further refining the AI model and incorporating advanced computational techniques, the researchers anticipate unlocking new possibilities for crystal structure prediction and molecular analysis.
The integration of artificial intelligence in chemistry represents a paradigm shift in the way researchers approach complex scientific challenges. The development of AI applications such as PhAI underscores the transformative potential of technology in streamlining processes, improving accuracy, and advancing scientific discovery in the field of chemistry. As we look towards the future, the synergy between human expertise and AI capabilities holds the promise of unlocking new frontiers in chemical research and innovation.

Leave a Reply