The issue of carbon emissions and its impact on climate change has been a pressing concern for scientists and environmentalists worldwide. The traditional methods of producing energy from fossil fuels only exacerbate this issue by introducing more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. However, researchers at McGill University have developed a groundbreaking catalyst that could potentially change the game when it comes to energy production.
The Role of Copper Nanoclusters
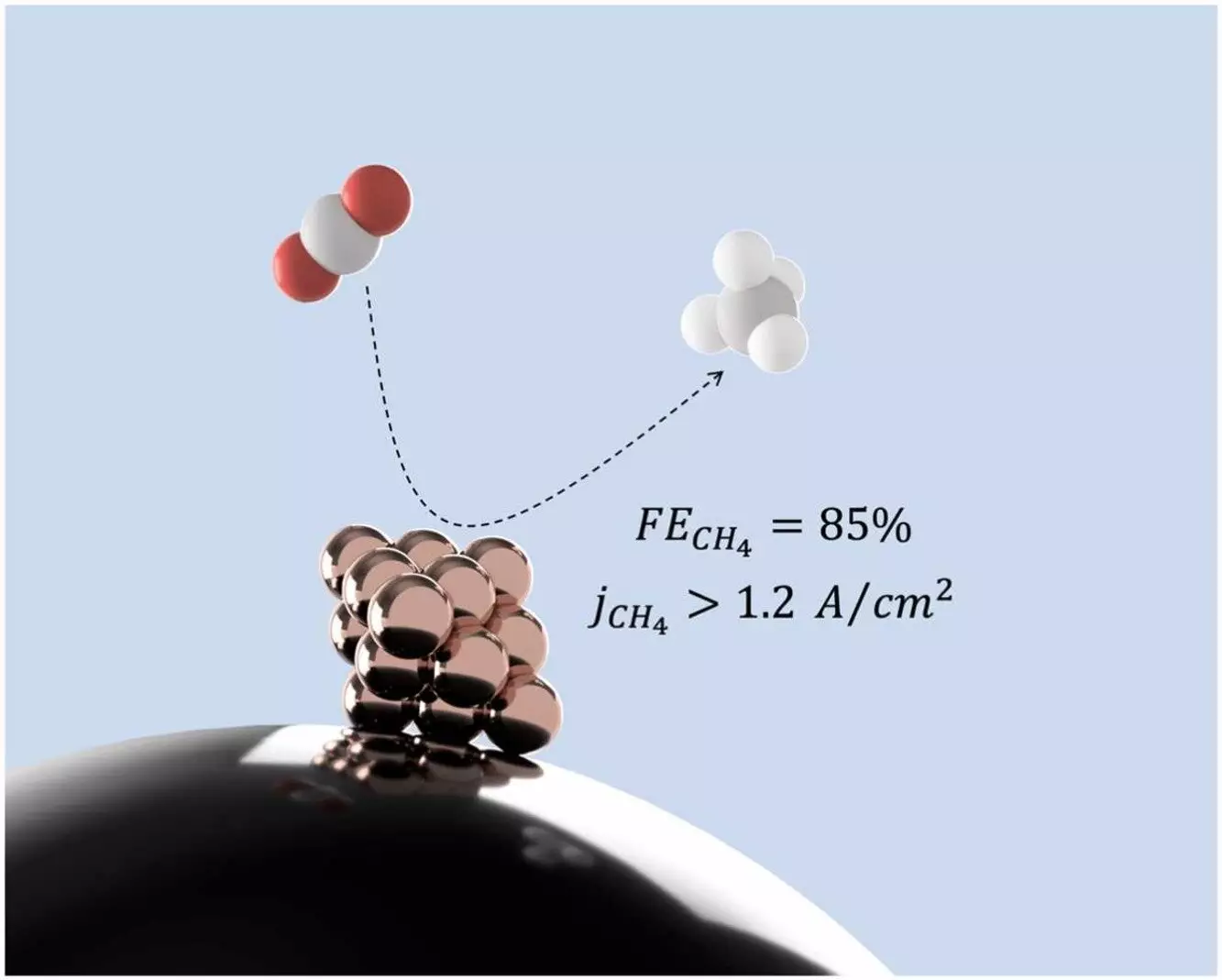
The catalyst designed by McGill University researchers utilizes tiny pieces of copper called nanoclusters to convert carbon dioxide into methane. This process, known as electrocatalysis, offers a cleaner and more sustainable source of energy. Unlike traditional methods, electrocatalysis does not contribute to the increase in carbon emissions, making it a promising solution in the fight against climate change.
One of the key benefits of using copper nanoclusters in the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane is the creation of a closed “carbon loop.” This means that any carbon dioxide released during the use of methane can be captured and recycled back into the production of methane. This innovative approach ensures that no additional carbon dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere, promoting a more sustainable energy production process.
Through their research, the team discovered that extremely small copper nanoclusters are particularly effective in producing methane. The size and structure of the catalyst play a crucial role in determining the outcome of the reaction. By focusing on the optimization of catalyst size, the researchers hope to further enhance the efficiency of the process and explore its potential for large-scale industrial applications.
Looking Towards the Future
The researchers at McGill University, in collaboration with the Canadian Light Source, are committed to advancing their catalyst to make it more efficient and practical for widespread use. Their ultimate goal is to revolutionize the way we produce energy by leveraging clean and sustainable technologies. With further developments and refinements, the potential for producing clean and renewable energy through carbon transformation could pave the way for a greener and more environmentally friendly future.

Leave a Reply