The landscape of technology is rapidly evolving, especially with the advent of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, which increasingly permeate our daily interactions and decision-making processes. These sophisticated AI systems are designed to analyze and generate human-like text by leveraging extensive datasets and advanced deep learning techniques. A recent study published in Nature Human Behaviour sheds light on both the opportunities and risks associated with LLMs, especially concerning their impact on collective intelligence—the capacity of groups to leverage shared knowledge and skills. Researchers from the Copenhagen Business School and the Max Planck Institute for Human Development spearheaded this study, providing insight into how LLMs can enhance and potentially diminish our collective deliberative capacities.
Understanding Collective Intelligence in the Age of AI
Collective intelligence is a term used to describe how groups can outperform individuals, even experts, by combining their unique skills and knowledge. This phenomenon is apparent in varied settings ranging from small teams in business environments to large-scale collaborations like Wikipedia—showcasing the potential of people working together. As we navigate the complexities of modern challenges, the utility of collective intelligence becomes increasingly vital. The integration of LLMs offers intriguing possibilities for enhancing this capacity further, particularly in fostering inclusivity and accelerating problem-solving processes.
The researchers identify several potential advantages of utilizing LLMs in collective processes. One of the most significant benefits is increased accessibility. Language models have the ability to translate and facilitate communication across linguistic and cultural barriers, enabling a more diverse range of participants to engage in discussions. This widening of participation can enhance the richness of contributions from various backgrounds, ultimately leading to more nuanced and effective decision-making.
Additionally, LLMs can act as accelerators for idea generation. By summarizing diverse opinions, generating relevant information, and helping to clarify complex topics, language models can play a crucial role in shaping discussions. This ability to synthesize large volumes of information can streamline processes and foster consensus—leading to enhanced outcomes in collective endeavors.
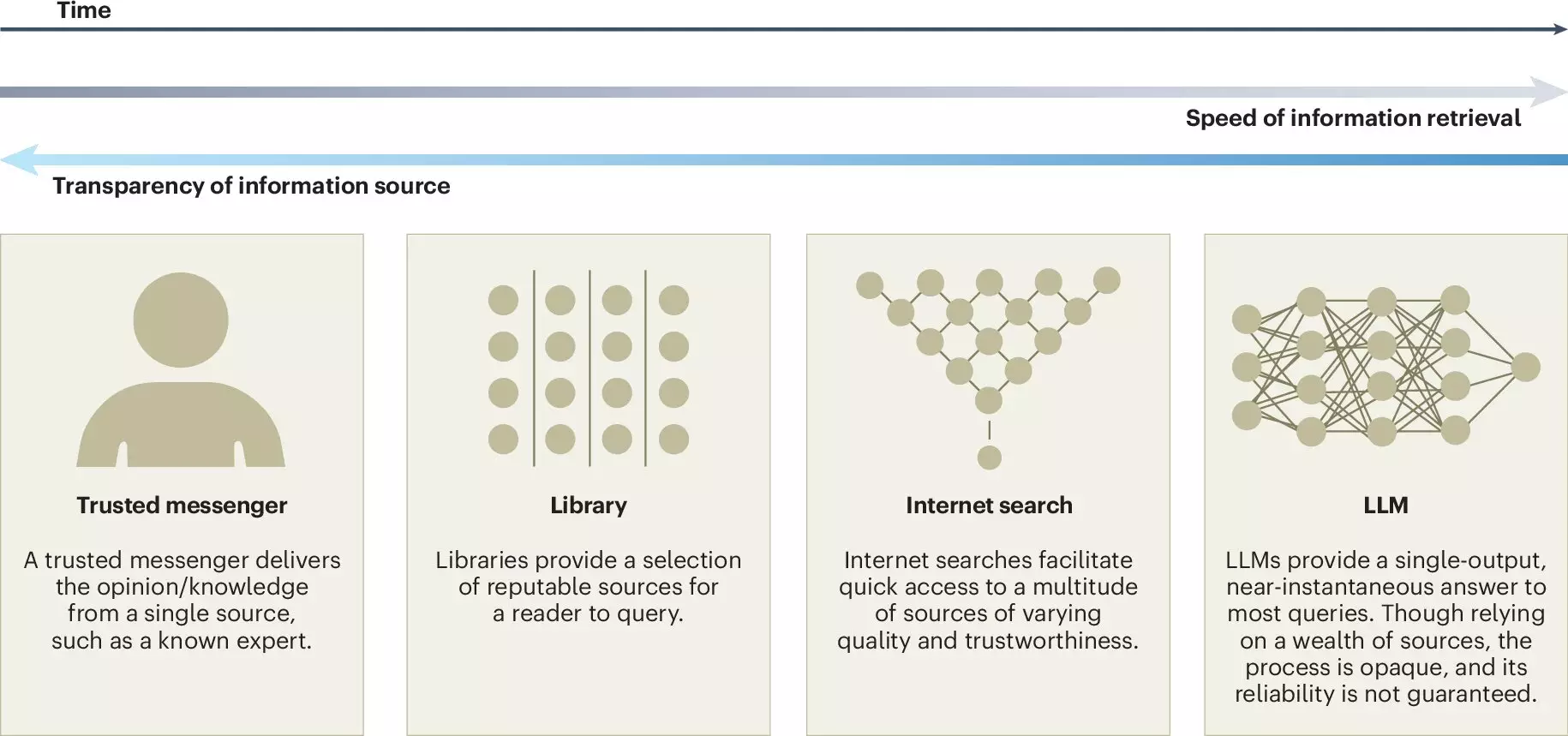
Despite the promising prospects of integrating LLMs into collective intellectual environments, significant risks accompany their deployment. One of the most pressing concerns relates to user dependence on proprietary models, which can undermine established knowledge commons like Wikipedia and Stack Overflow. If collective resources are overshadowed by LLM-generated information, the diversity and richness of online knowledge may be compromised.
Moreover, the potential for false consensus and pluralistic ignorance looms large. Because LLMs are trained on existing online content, they might not accurately reflect minority viewpoints, creating a distorted perception of consensus. This issue is critical, as marginalized perspectives could be further sidelined, resulting in an incomplete understanding of issues at hand and fostering misunderstanding among users.
The Call for Transparency and Accountability in LLM Development
Given the profound implications of LLMs, the researchers emphasize the need for transparency in their development. They advocate for clear disclosure of training data sources and suggest implementing external audits to monitor the models’ efficacy and fairness. Such measures would provide valuable insights into how LLMs are constructed and the implications of their usage, allowing for better management of their impact on collective intelligence.
The study also addresses the role of humans in the development of LLMs, stressing the necessity for diverse representation in training datasets. By ensuring a variety of voices and perspectives are included, developers can mitigate risks of homogenization and strive to create AI systems that reflect a broader spectrum of human experiences and ideas.
The article raises important research queries regarding LLMs and their relationship with collective intelligence. Key questions include how to prevent the homogenization of knowledge and how to divvy up credit and responsibility when collective outcomes involve LLMs. These issues necessitate further exploration, particularly as LLMs become more entrenched in societal decision-making.
While LLMs hold the potential to significantly enhance collective intelligence by improving accessibility, generating ideas, and summarizing information, careful consideration is warranted regarding their risks. Establishing a framework of transparency, accountability, and diverse representation in LLM development is crucial. The collaborative efforts of researchers and policymakers can ensure that these technologies are beneficial rather than detrimental to collective human endeavors.

Leave a Reply