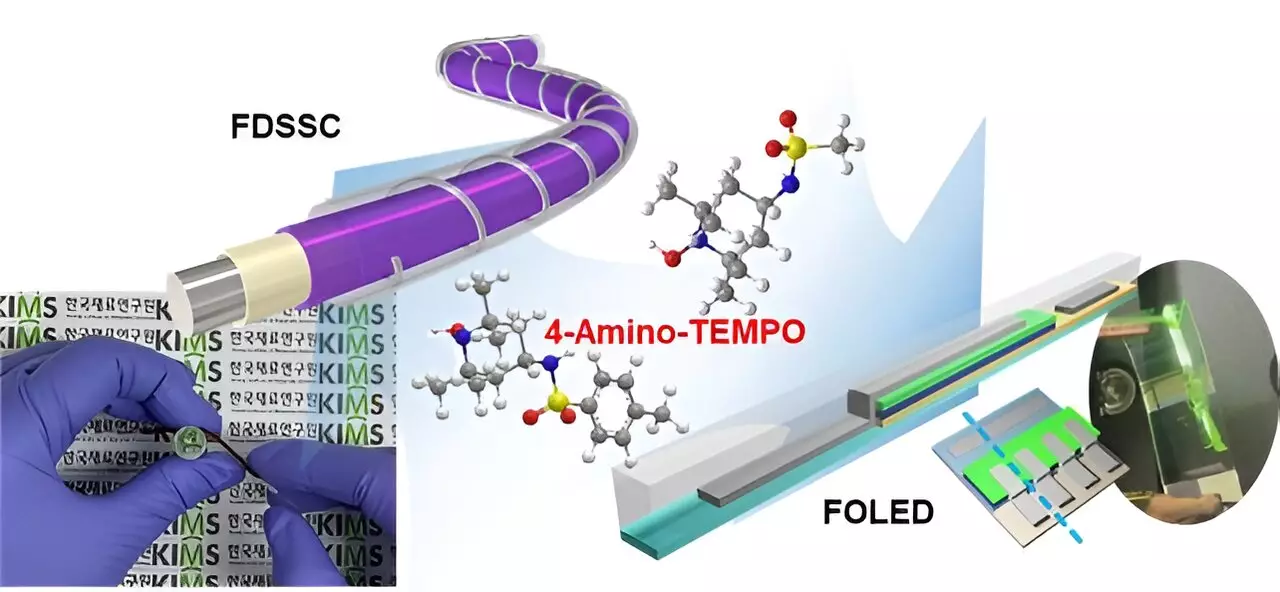
In a groundbreaking joint research effort, a team of scientists has recently developed a new 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative with remarkable photocatalytic properties. This innovative material has been successfully utilized to create high-performance and stable fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped organic light-emitting diodes (FOLEDs), marking a significant advancement in electronic device technology.
One of the key advantages of the newly developed 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative is its ability to enhance the performance of both FDSSCs and FOLEDs simultaneously. Unlike conventional materials that are complex to synthesize and difficult to mass produce, the 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative offers a simple synthesis process and can be produced in large quantities. Moreover, devices fabricated with this derivative have shown more than a 20% improvement in performance compared to traditional electronic components.
The research team, led by Professor Chul-jin Ahn’s team at Changwon National University, along with Dr. Jae-Ho Kim and Dr. Myung-kwan Song from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials in the Surface & Nano Materials Division, worked collaboratively to design and synthesize a material with photocatalytic properties. This material not only enhances the efficiency of FDSSCs but also demonstrates high stability in both air and moisture, making it ideal for producing cutting-edge electronic devices.
The Versatility of 4-Amino-TEMPO Derivatives
4-Amino-TEMPO derivatives have a wide range of applications in the field of electronic devices, including their use as solid electrolytes in lithium batteries, catalysts, solar cells, and organic light-emitting diodes. What differentiates this technology from others is its cost-effectiveness and the ease of mass production. With the ability to offer multifunctionality rather than single-functionality, these derivatives are poised to revolutionize various electronic applications.
The Economic Impact of Mass Production
Not only do 4-Amino-TEMPO derivatives enable mass production at a low cost (less than 1 million won per 100g), but they also have the potential to generate significant economic benefits for electronic device companies. Leveraging this technology for local and mass production could pave the way for unprecedented growth in the electronic device industry. Dr. Myung-kwan Song, the lead researcher of the study, emphasized the importance of multifunctional materials in enhancing performance and reliability in electronic devices.
The development of 4-Amino-TEMPO derivatives represents a major breakthrough in electronic device technology. With their ability to improve the performance and stability of FDSSCs and FOLEDs, these innovative materials have the potential to revolutionize the electronic device industry and drive economic growth in the future.

Leave a Reply