Recent breakthroughs in the field of synthetic immunology have been illuminated by researchers at Heidelberg University’s Institute of Organic Chemistry and Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology. Their pioneering work has led to the development of a cutting-edge chemical process that facilitates the rapid production of modified peptides through the incorporation of boronic acids. This advancement not only marks a significant step forward in peptide synthesis but also enhances our understanding of how these molecular structures can interact with immune systems for therapeutic purposes.
Peptides are essential biomolecules, composed of amino acids, that serve as critical components within cellular architecture. They play a vital role in immunology, acting as key mediators that relay immunological signals, thus informing the body’s immune response. The specific arrangement and types of amino acids within these peptides dictate whether a substance is recognized as foreign, subsequently triggering an immune response. Marius Werner, a doctoral candidate involved in this research, emphasizes that effective therapeutic protocols, including vaccinations, often revolve around the strategic use of peptides.
The Promise of Boronic Acids
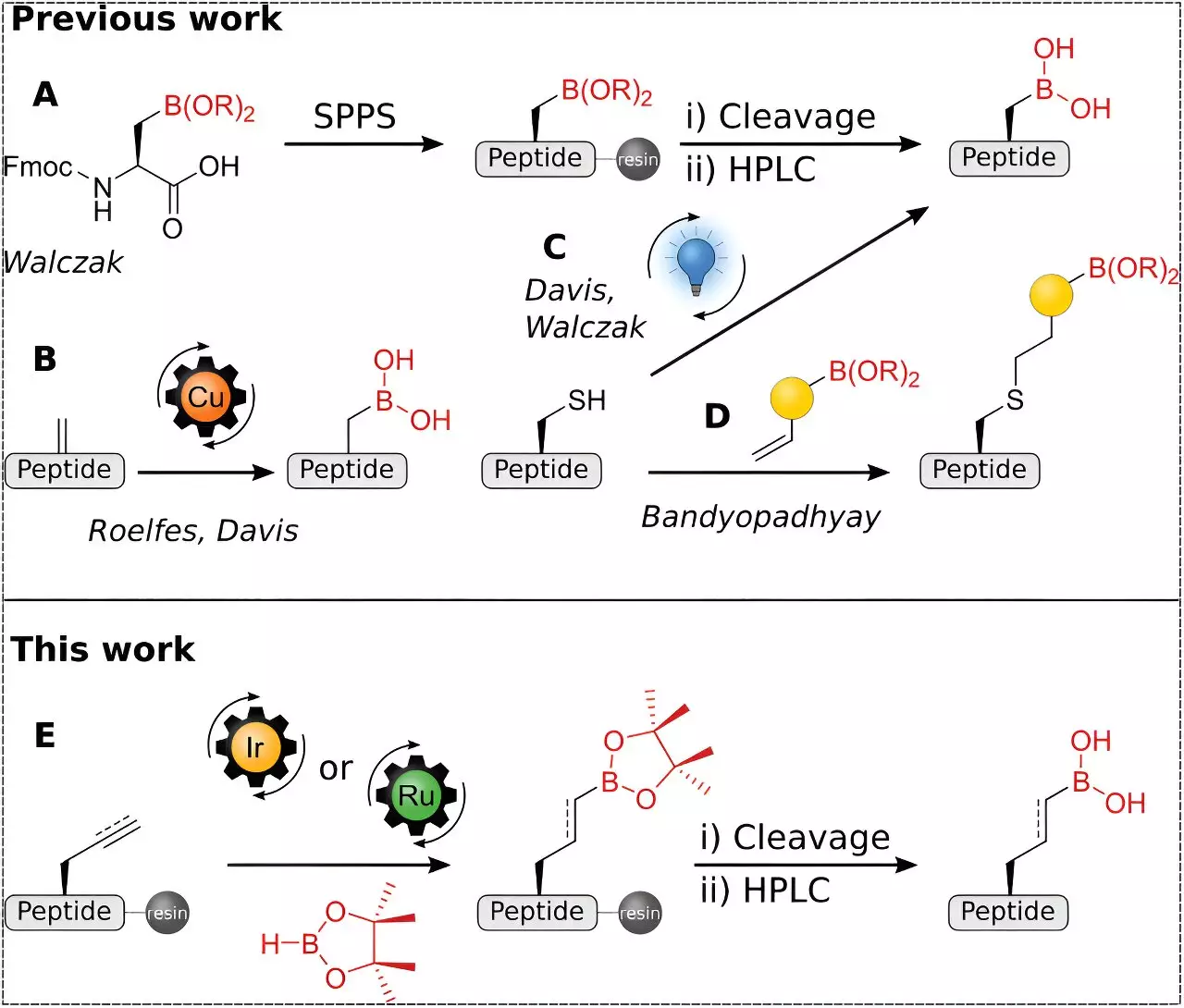
Boronic acids have emerged as a focal point of interest in this innovative study due to their unique interaction profiles with immune cells and other biological targets. The current research, recently published in *Advanced Science*, showcases the synthesis of bioactive peptide boronic acids, a feat accomplished by the hydroboration of peptide alkenes and alkynes that were bound to a resin. This specific chemical transformation allows for the creation of novel peptide configurations that were previously challenging to synthesize.
Under the leadership of Junior Professor Dr. Franziska Thomas and Professor Dr. Christian Klein, the team’s approach highlights how the incorporation of boronic acid groups into peptides opens doors for further chemical modifications. This flexibility suggests that diverse structural variations can be easily achieved, making these peptides adaptable for a variety of immunological applications. This characteristic could pave the way for significant advancements, particularly in immunotherapy, potentially augmenting the body’s natural defenses against disease processes such as tumors.
Engineering Immune Responses Against Tumors
A noteworthy application of these modified peptides lies in their potential to engage the immune system against cancerous cells. According to Professor Klein, the new class of peptide boronic acids could be instrumental in inciting an immune reaction against tumor cells, harnessing the body’s intrinsic capabilities to combat malignancy. Such advancements could revolutionize cancer treatment paradigms by promoting the development of personalized immunotherapeutic strategies tailored to individual patients.
In addition to immunotherapy applications, the researchers propose the innovative use of peptide boronic acids in targeted drug delivery systems. By acting as anchors, boronic acids can facilitate the selective binding of peptides to nanoparticles designed for transportation within the body. These engineered particles could be crafted to release their peptide cargo in specific tissues or cells, optimizing therapeutic outcomes in targeted areas, particularly those related to the immune response.
The implications of this research extend beyond immediate clinical applications. The prospect of using peptide boronic acids in conjunction with small, biodegradable implants that can dissolve within the body introduces a new frontier in pharmaceutical delivery. As scientists continue to explore these possibilities, the potential for peptide boronic acids to reshape treatment methodologies becomes increasingly apparent.
The ongoing investigations at Heidelberg University signify a transformative movement within the realm of synthetic immunology. The rapid synthesis and diversity of peptide boronic acids offer promising avenues for both therapeutic and prophylactic measures against diseases. As researchers delve deeper into this uncharted territory, the impact of these modified molecules could redefine our approach to immunotherapy, drug delivery, and beyond, affirming the significance of boronic acids in contemporary biochemistry.

Leave a Reply