The study conducted by scientists from China delves into the intricate world of short peptide chains and how they aggregate, shedding light on a process crucial for drug stability and material development. Peptides, which are short chains of amino acids, are integral to various bodily functions such as building structures, facilitating chemical reactions, and bolstering the immune system. The interaction and aggregation of amino acids within a protein ultimately determine its three-dimensional structure and specific function.
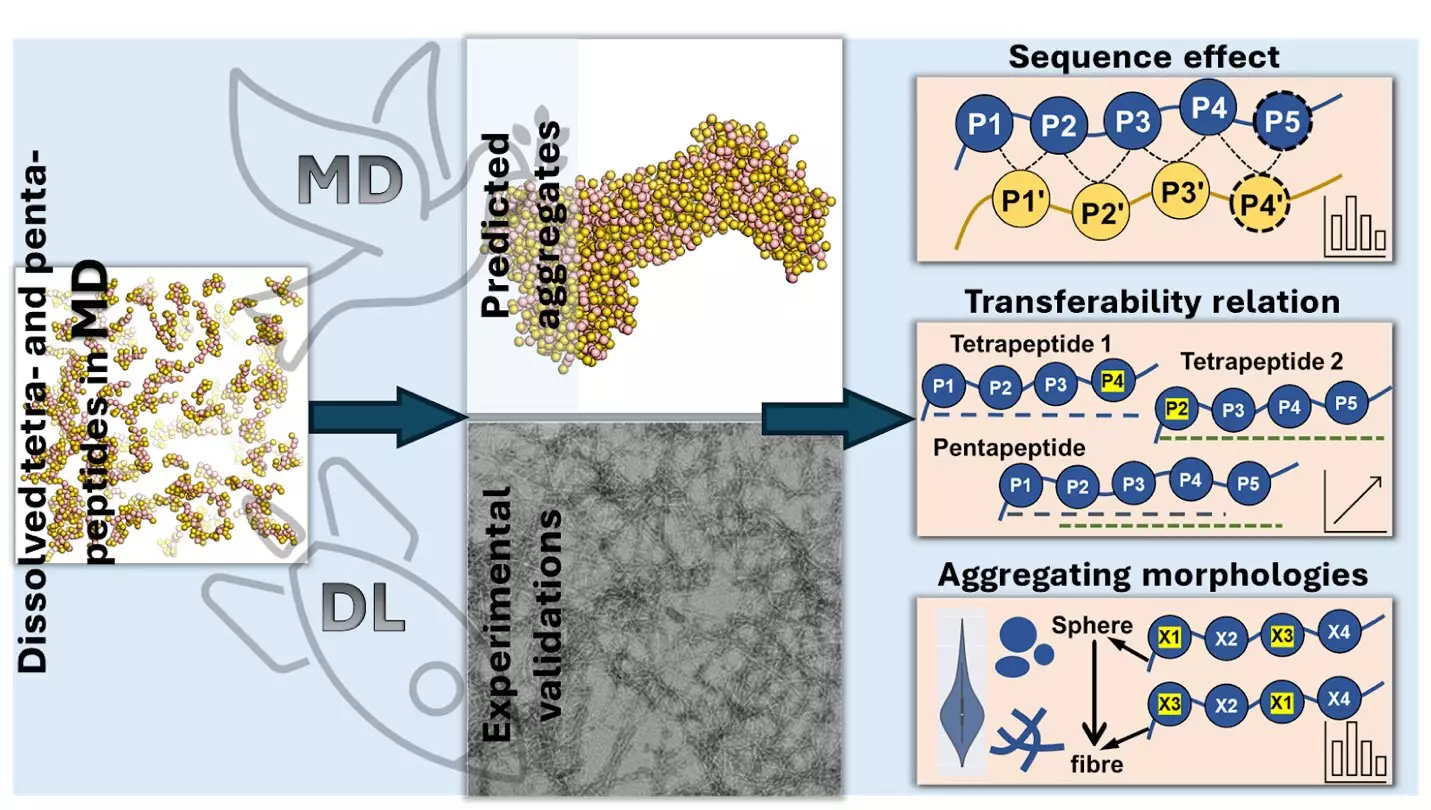
To unravel the mysteries of peptide aggregation, the research team employed molecular dynamics simulations in combination with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies. Deep learning models like Transformer Regression Networks were used to predict the aggregation behavior of tetrapeptides and pentapeptides – peptides composed of four and five amino acids, respectively. Through analysis of 160,000 tetrapeptides and 3.2 million pentapeptides, the study uncovered key insights into the role of specific amino acids in enhancing or inhibiting aggregation. Aromatic amino acids like tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine were found to significantly promote aggregation, particularly when located at the C-terminus of the peptide chain.
The research demonstrated that the sequence of amino acids plays a critical role in peptide aggregation. The addition of aromatic amino acids at the end of the peptide chain was shown to increase aggregation, while the presence of negatively charged amino acids at the beginning of the chain had the opposite effect. Furthermore, the positioning and types of amino acids influenced the shape of peptide clusters, with charged amino acids leading to long, thread-like structures and hydrophobic amino acids forming spherical clusters.
Dr. Wenbin Li, an assistant professor at Westlake University and corresponding author of the study, highlighted the significance of the findings in the fields of medicine, material science, and biotechnology. Understanding how peptides aggregate can aid in the development of new materials, design of stable drugs and drug delivery systems, as well as in elucidating diseases associated with peptide aggregation, such as Alzheimer’s disease. The study opens up avenues for advancements in biotechnology, including semiconductors, biosensors, and diagnostics, by ensuring the accuracy and consistency of these tools.
By incorporating AI techniques into the exploration of peptide aggregation, the research paves the way for innovative approaches to biochemistry, materials science, and computational biology. Dr. Jiaqi Wang, first author of the study and an assistant professor at Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU), emphasized the potential of the research to revolutionize the understanding and management of peptide aggregation. The insights gained from the study have far-reaching implications for various scientific disciplines, showcasing the power of integrating AI into scientific discovery processes.

Leave a Reply