In our rapidly evolving technological landscape, efficient electronic devices are indispensable. From smartphones to electric vehicles, the demand for reliable performance is ever-increasing, with efficiency and durability being top priorities for manufacturers. However, the growing complexity of modern electronics poses a significant challenge: obtaining accurate temperature measurements of internal components. Understanding the thermal dynamics of materials used in electronics is crucial not just for optimizing performance but also for ensuring the longevity and safety of these devices.
The temperature of electronic components directly influences their performance; excessive heat can lead to malfunctions or failures. Traditionally, methods such as thermocouples and infrared sensors have been employed to gauge the temperature inside electronic devices. While these technologies have their advantages, they often fall short in providing the rapid and precise data necessary for advanced applications. This gap has long been a focal point for researchers and engineers seeking to innovate and enhance the reliability of electronics.
Introducing Neutron Resonance Absorption
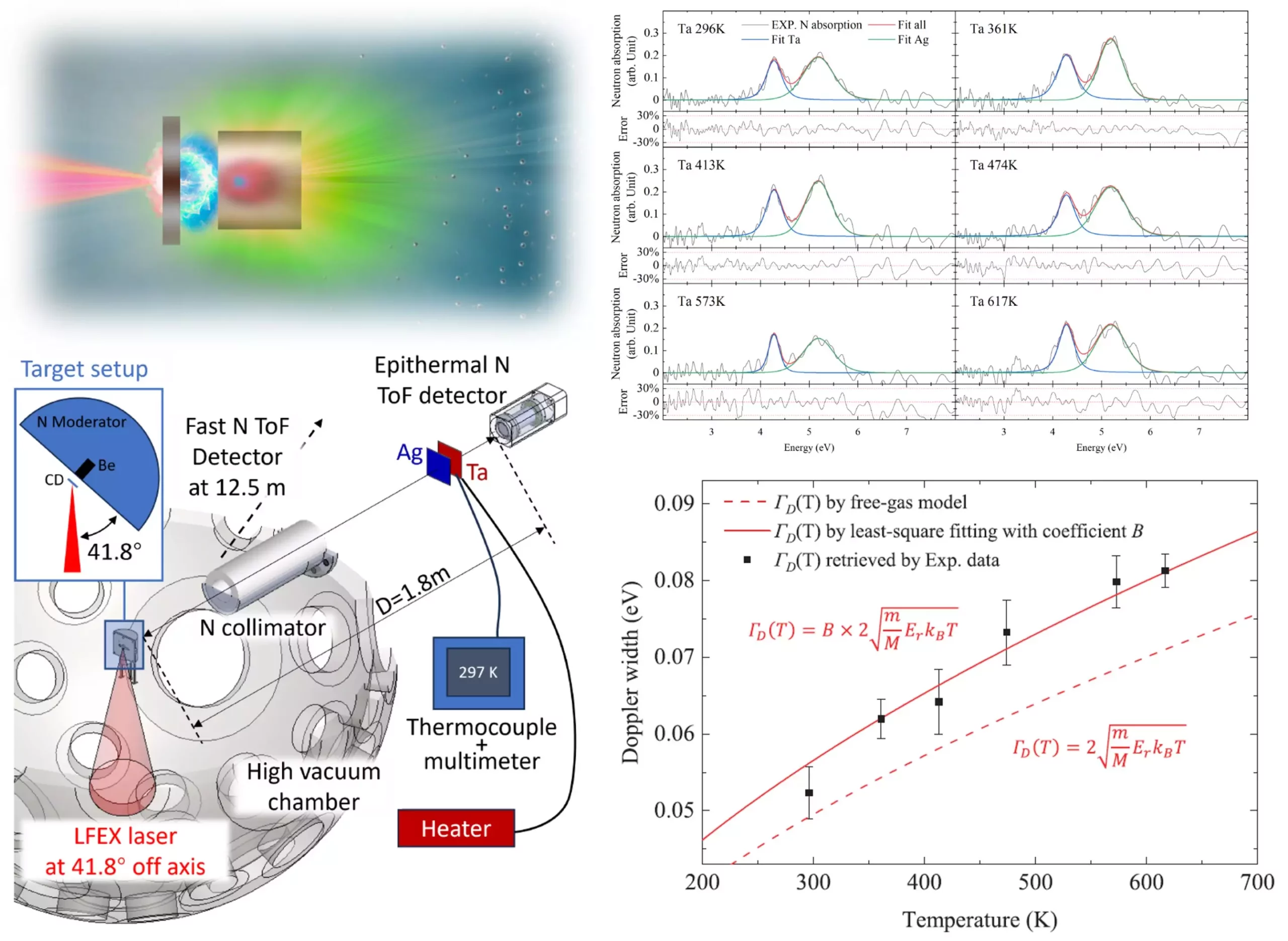
A groundbreaking study from Osaka University has introduced a novel approach to addressing the issue of reliable temperature measurements through the utilization of neutron resonance absorption (NRA). This innovative technique provides a direct measurement of temperature that promises to transform how we monitor and understand electronic devices. Unlike traditional methods, NRA allows researchers to discern temperature variations with an impressive speed that could lead to significant advancements in the field.
The process involves using high-intensity laser beams to generate neutrons, which are then decelerated to low energy levels before being directed at the sample materials. This method was meticulously tested using tantalum and silver plates, yielding exceptional insights into the materials’ properties and thermal dynamics. The significance of this advancement lies in its ability to provide instantaneous temperature readings, an essential requirement for real-time applications in electronics.
Non-Destructive and Rapid Measurement
One of the standout advantages of the NRA technique, as articulated by lead author Zechen Lan, is its non-destructive nature. This means that it can be employed during the operational phase of electronic devices, enabling continuous monitoring without compromising their integrity. The ability to measure temperatures within a narrow time frame—about 100 nanoseconds—makes this method particularly valuable. This near-immediate response facilitates rapid adjustments and diagnostic assessments, enhancing our understanding of how electronic systems operate under different conditions.
Senior author Akifumi Yogo highlighted the implications of this research, indicating that the high temporal resolution of the new measurement system could lead to unprecedented analysis of electronic devices. Identifying normal operating conditions and recognizing abnormalities could empower engineers to innovate and refine their designs, ensuring that future electronics meet both performance and safety standards.
The Compact Future of Temperature Measurement Devices
Another remarkable achievement of this study is the development of a measurement device that is significantly smaller than existing alternatives. The compact nature of this technology means that it can be easily integrated into various laboratory settings, democratizing access to sophisticated measurement capabilities. Smaller devices can stimulate widespread adoption and experimentation across research institutions and industries alike, accelerating advancements in electronic technologies.
The implications of this compact and efficient measurement tool extend beyond mere temperature assessments; they may pave the way for enhanced research into material science, helping to uncover fundamental insights into how different materials behave under thermal stress. By understanding these dynamics better, researchers can push the boundaries of material design to produce new electronics that are not only thermally stable but also more efficient and environmentally friendly.
A Step Towards the Future of Electronics
The introduction of neutron resonance absorption for rapid temperature measurement heralds a new era in the field of electronics. As technology continues to advance, maintaining a focus on efficiency and reliability will be paramount. This innovative technique not only enhances our capacity to monitor electronic devices but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in both materials and design. The seamless interplay between advanced measurement techniques and real-time data acquisition will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the evolution of electronics, ensuring they meet the demands of an increasingly complex digital world. The fusion of speed, accuracy, and the capability for non-destructive testing encapsulates the potential for revolutionary changes in how we engineer and use electronics moving forward.

Leave a Reply