The essence of life is water, and the necessity for clean drinking water has never been more critical. With the global population rising at an alarming rate, the strain on our water sources intensifies. Communities worldwide face the daunting challenge of ensuring access to safe drinking water, which is fundamental to health and well-being. Traditional methods for purifying water often fall short in efficiency and specificity, resulting in the unintended removal of beneficial minerals along with harmful pollutants. As we encounter this pressing global issue, innovative approaches to water purification are essential to safeguard the health of populations and ecosystems alike.
Nature’s Ingenious Mechanisms: Lessons from Phytochelatin
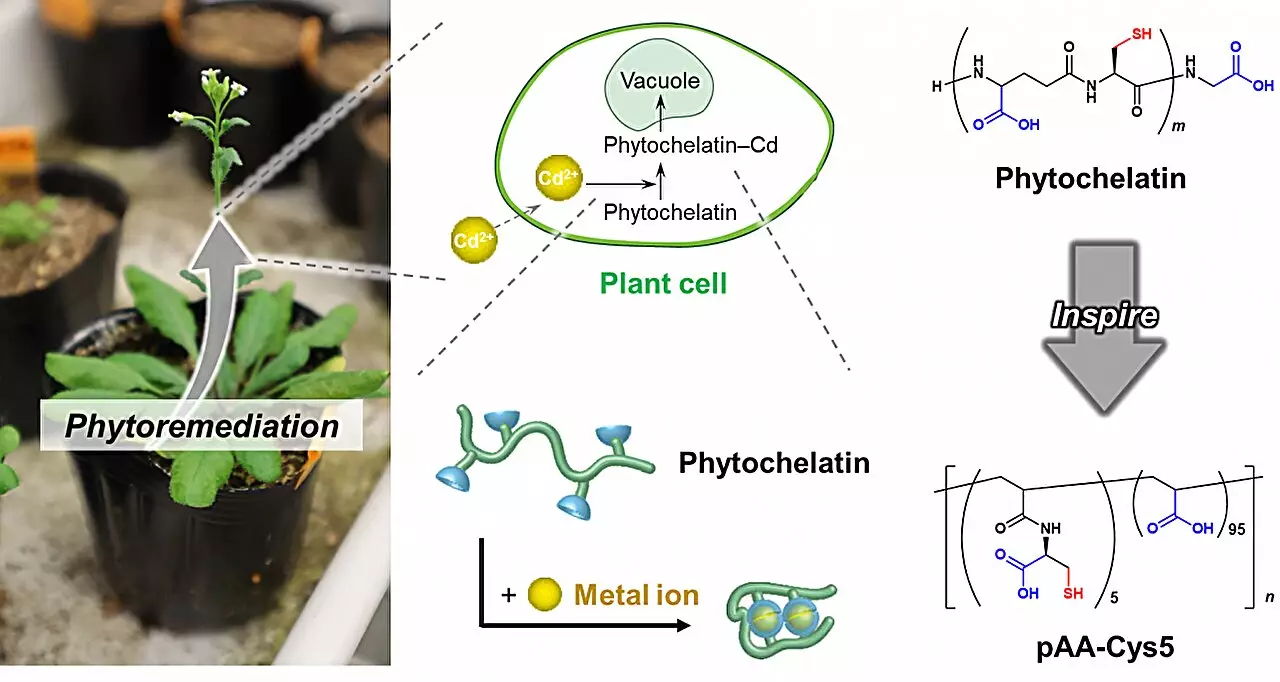
Recent advancements in water treatment technology hold tremendous promise, particularly those inspired by the intricate mechanisms present in nature. A notable breakthrough arises from research conducted by the HeKKSaGOn Alliance, which brings together experts from esteemed institutions such as Kyoto University, Osaka University, and Heidelberg University. Central to their findings is a plant-derived protein known as phytochelatin, which specifically targets and binds to harmful heavy-metal ions like cadmium. This specificity is crucial, as prevailing purification methods often indiscriminately remove various ions, hindering their effectiveness in delivering safe water.
Phytochelatin exemplifies how nature has fine-tuned its machinery to address environmental threats. By efficiently sequestering toxic ions, this protein protects plants from heavy metal toxicity—a feat that researchers have now leveraged to formulate a polymer with enhanced purification capabilities. The structured approach has not only captured the scientific imagination but also highlights the need to rethink conventional methodologies in water treatment.
Innovative Polymer Development: The Science Behind the Breakthrough
The research team’s inquiry into phytochelatin revealed the strategic arrangements of two key building blocks: carboxylate and thiolate groups. These components are instrumental in the polymer’s ability to selectively bind to harmful cadmium ions. By synthesizing a polymer that mimics these structures, researchers have harnessed the natural efficiency of plant proteins to develop a new class of water purifying agents.
Attached to silica beads and cellulose membranes, this polymer can concentrate contaminants into minuscule volumes. When contaminated water flows past the polymer within this novel flow-through system, the polymer effectively extracts cadmium ions, restoring the water to an approved drinking level within a remarkable timeframe of just one hour. This efficiency dramatically contrasts with traditional methods, underscoring the potential for this innovation to redefine water purification.
Targeted Actions: The Specificity Advantage
One of the pivotal features of this new polymer is its high specificity for cadmium ions compared to essential metal ions, such as magnesium and calcium. This characteristic positions the polymer as a safe and efficient alternative to existing water treatment technologies. Furthermore, the polymer displays a significant affinity for other hazardous metals, such as mercury, amplifying its capacity as a versatile solution for a range of heavy-metal contaminants.
Motomu Tanaka, the senior author of the study, emphasizes the sophistication of bacterial mechanisms evolved over time, stating, “Biology doesn’t make nonsense.” The successful adaptation of these biological principles into synthetic materials not only showcases an exemplary fusion of research and application, but it captures a pathway to a more profound understanding of the interactions between pollutants and purifying agents.
A Vision for the Future: Toward Sustainable Water Solutions
The newfound abilities of this polymer-derived from nature’s own defenses signify a transformative step towards sustainable water purification solutions. The implications extend beyond mere efficiency; they symbolize a broader movement towards embracing biomimicry in technology. As the global community continues to grapple with water scarcity and contamination, innovative approaches that draw upon natural systems will become vital in ensuring safe drinking water for all.
In a world where environmental health and human well-being are increasingly intertwined, the insights gained from observing and replicating nature could pave the way for novel solutions. As we forge ahead, the quest for clean drinking water is more than a scientific endeavor; it is a moral obligation to uphold the dignity of life across the planet.

Leave a Reply