In the fast-paced urban environments of today, the reliance on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) such as the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) for high-precision positioning is increasingly hampered by multi-layered challenges. Signal blockages caused by skyscrapers, overpasses, and other urban obstacles significantly diminish the performance of GNSS technologies. Furthermore, interference from surrounding electronic devices complicates signal clarity, resulting in inaccuracies that undermine the effectiveness of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) positioning systems. Traditional methods of overcoming these obstacles, including the use of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, have proven limited in delivering the precision necessary for critical applications.
The introduction and widespread adoption of 5G technology mark a pivotal moment in addressing these urban navigation challenges. With its unprecedented speed, bandwidth, and signal density, 5G presents a more promising alternative for enhancing GNSS functionalities. Researchers from Tsinghua University recently showcased an innovative solution that leverages 5G capabilities with the BDS RTK system, aiming to redefine the potential for positioning technologies in dense urban landscapes. Their work, recently published in the journal Satellite Navigation, unveils the efficacy of combining 5G signals with conventional satellite data to address historic deficiencies in urban positioning.
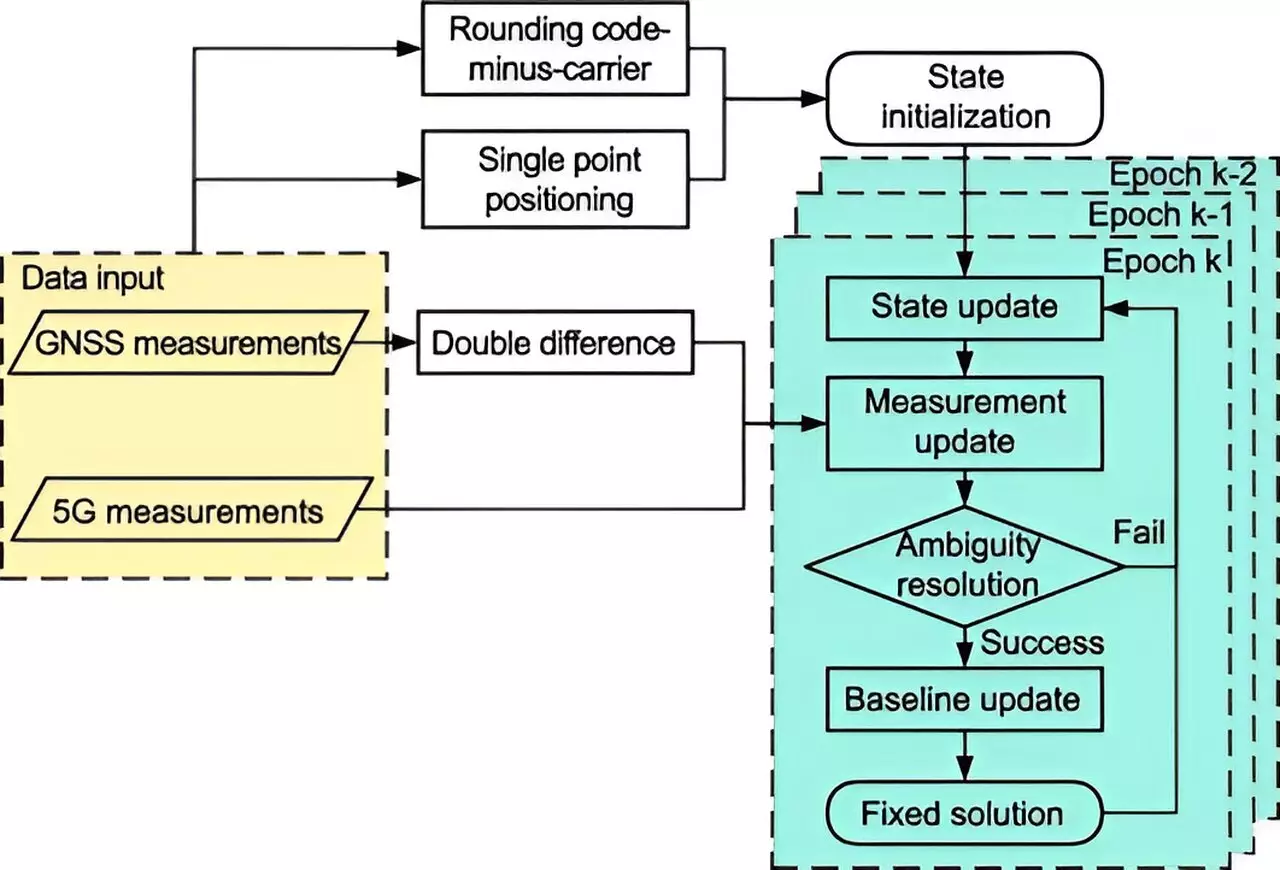
At the core of the new 5G-assisted BDS RTK positioning system is a sophisticated implementation of an extended Kalman filter and advanced ambiguity resolution techniques. These algorithms are designed to synthesize data from both 5G networks and satellite sources, paving the way for enhanced accuracy despite the common impediments of urban environments. The results of their experimentation are promising, showcasing substantial improvements in positional accuracy. Specifically, the research indicated a reduction in spatial errors by 48% when utilizing Full Ambiguity Resolution (FAR) mode and 18.8% in Partial Ambiguity Resolution (PAR) mode. Such enhancements highlight the potential of this innovative approach to substantially elevate high-precision positioning standards.
The effectiveness of the 5G-enhanced BDS RTK system is underscored by improvements in fixing rates— which represent the system’s ability to reliably determine precise locations. In FAR mode, the fixing rates rose from 11.11% to 13.93%, while in PAR mode, rates escalated from 32.58% to 44.43%. These statistics indicate a marked enhancement in reliability, paving the way for broader applications in areas such as autonomous vehicle navigation, public safety, and smart city infrastructure.
Dr. Tengfei Wang from Tsinghua University emphasizes the significance of this integration, declaring that the fusion of 5G with BDS RTK tackles persistent urban challenges by improving both signal quality and satellite visibility. As 5G networks continue to proliferate, grounding this adaptive positioning solution becomes increasingly feasible, promising a future where urban navigation becomes more reliable and precise.
The integration of 5G with BDS RTK positioning systems is set to transform urban navigation, offering a scalable solution for the ever-growing demands of smart cities. Ongoing research will focus on testing this system across various real-world conditions to refine and enhance its performance. Ultimately, the ramifications of this innovation extend beyond mere accuracy improvements; they create opportunities for more sophisticated and efficient urban navigation solutions that can redefine how we interact with complex city landscapes in the future.

Leave a Reply