Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have become essential materials for numerous applications due to their customizable structures and unique properties. Traditionally, MOFs have been designed using either a bottom-up or top-down approach, limiting the scope of potential structures that can be created. However, a recent study published in the journal Nature Synthesis introduces a groundbreaking strategy known as the “Up-Down Approach,” which combines elements of both methodologies to accelerate the discovery and synthesis of MOFs.
The Up-Down Approach developed by Professor Wonyoung Choe and his research team at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in South Korea offers a fresh perspective on MOF design. By focusing on exploring metal clusters before selecting organic ligands, this approach allows for a wider range of structural possibilities that were previously unattainable. This innovative strategy overcomes the limitations of traditional methods, providing researchers with new opportunities to discover novel MOF structures with unique properties.
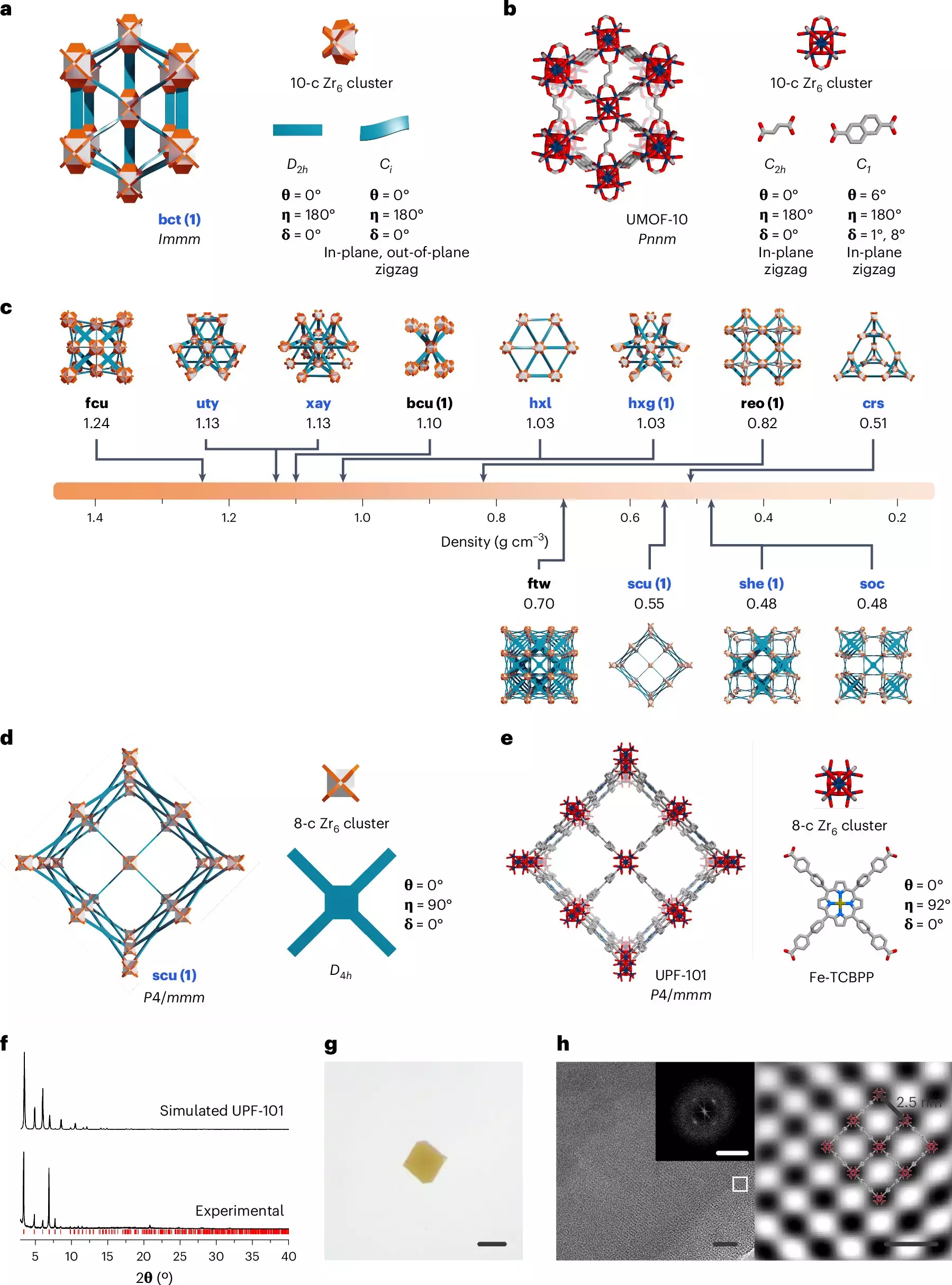
Through the implementation of the Up-Down Approach, the research team was able to identify and synthesize 26 new zirconium-based MOFs, known for their exceptional chemical stability. By successfully creating two of these newly discovered structures, the effectiveness of this novel approach was clearly demonstrated. Additionally, the team utilized a “Ribbon Representation” technique to visualize the geometric features of organic ligands, further enhancing the precision and efficiency of the design process.
Jiyeon Kim, the first author of the study, highlighted the significance of the Up-Down Approach in accelerating the exploration and development of new materials with diverse chemical properties. This method not only improves the efficiency of material research but also opens up possibilities for the creation of innovative materials that can be applied across various fields, including catalysis, gas storage, and environmental remediation. Co-first author Dongsik Nam emphasized the potential impact of this research on expanding the chemical space of MOFs and broadening their scope of applications.
The introduction of the Up-Down Approach represents a major advancement in the field of MOF synthesis, offering researchers a powerful tool for discovering new materials with tailored properties. This innovative strategy has the potential to revolutionize the way MOFs are designed and synthesized, paving the way for the development of cutting-edge materials with a wide range of applications. With further research and exploration, the Up-Down Approach has the capability to drive the field of MOF research towards new horizons of discovery and innovation.

Leave a Reply