Robotic grippers have been a focal point for researchers worldwide in recent years, leading to the development of various designs that can pick up and manipulate different types of objects. Human-inspired grippers have shown significant promise in handling complex object manipulation tasks. However, many of these grippers rely on advanced mechanisms and sophisticated programming tools, making them less practical for large-scale deployment due to their high costs.
A team of researchers from Purdue University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have taken a different approach by developing a simpler yet equally effective robotic gripper. This gripper, which was detailed in a paper on the arXiv preprint server, has demonstrated the ability to handle intricate object manipulation tasks despite having fewer degrees of freedom (DOF) compared to humanoid robotic hands.
Bridging the Gap
Traditional high DOF dexterous robotic hands can tackle complex manipulation tasks, but their complexity makes them challenging to program and control. On the other hand, simpler one DOF parallel-jaw robotic grippers are easier to control but are limited to basic grasping tasks. The research team aimed to bridge the gap between these two types of grippers by designing a gripper with 5 DOF.
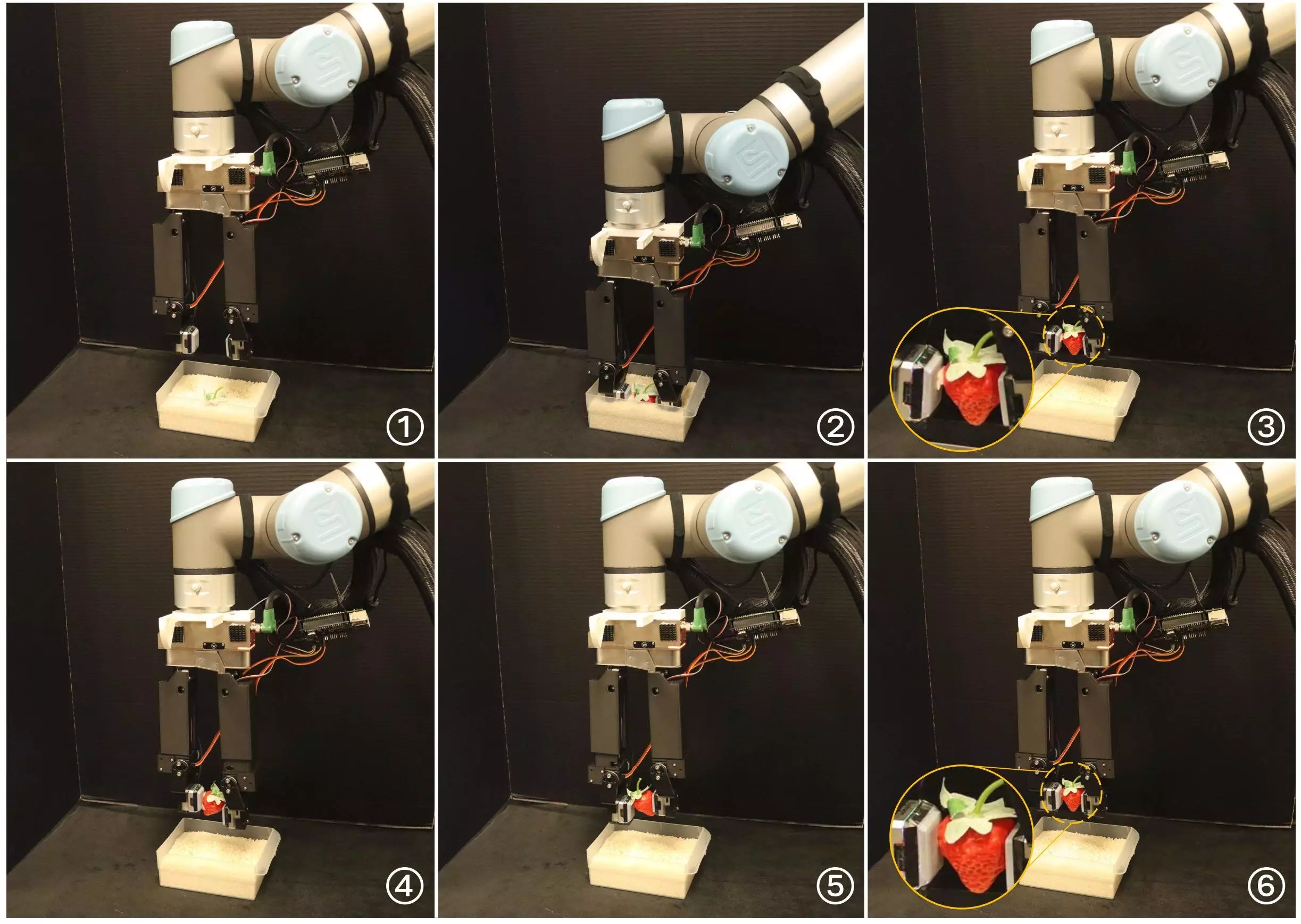
The newly developed gripper consists of two fingers attached to a gripper base, with a vision-based tactile sensor integrated into the left finger. This design allows the gripper to perform human-like in-hand manipulations by leveraging sensory data recorded by the tactile sensor. The gripper’s simple yet effective design, combined with its 5 DOF, enables it to achieve a high level of dexterity during manipulation tasks.
In a series of initial real-world experiments, the researchers evaluated the gripper’s performance and found that it surpassed the basic manipulation skills of grippers with fewer DOF. The gripper successfully completed tasks such as singulation and scooping, showcasing its ability to replicate human motions during object manipulation.
The research team sees great potential for further development and application of the robotic gripper in complex object manipulation tasks. The gripper’s design could serve as a foundation for the development of cost-effective and efficient robotic systems for a wide range of applications.
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to utilize the tactile gripper to tackle more challenging manipulation tasks that are currently beyond the capabilities of existing robotic grippers. By simplifying the controller design and enhancing the overall efficiency of robotic solutions, the team aims to pave the way for the widespread adoption of these advanced grippers in various industries.
The development of this new robotic gripper represents a significant step forward in the field of object manipulation technology. With its innovative design and impressive capabilities, this gripper has the potential to revolutionize the way robots interact with and manipulate objects in real-world settings.

Leave a Reply