The demand for wireless internet access has skyrocketed in recent years, leading to increased power consumption and carbon emissions globally. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, researchers are exploring innovative methods to support wireless communication while minimizing energy consumption. One such solution gaining traction is visible light communication (VLC), which utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to transmit data. A recent development by researchers at Central University (CU), IIDM, and CU J&K in India introduces a hybrid approach that combines VLC with radio frequency (RF) communication to create a more efficient wireless network.
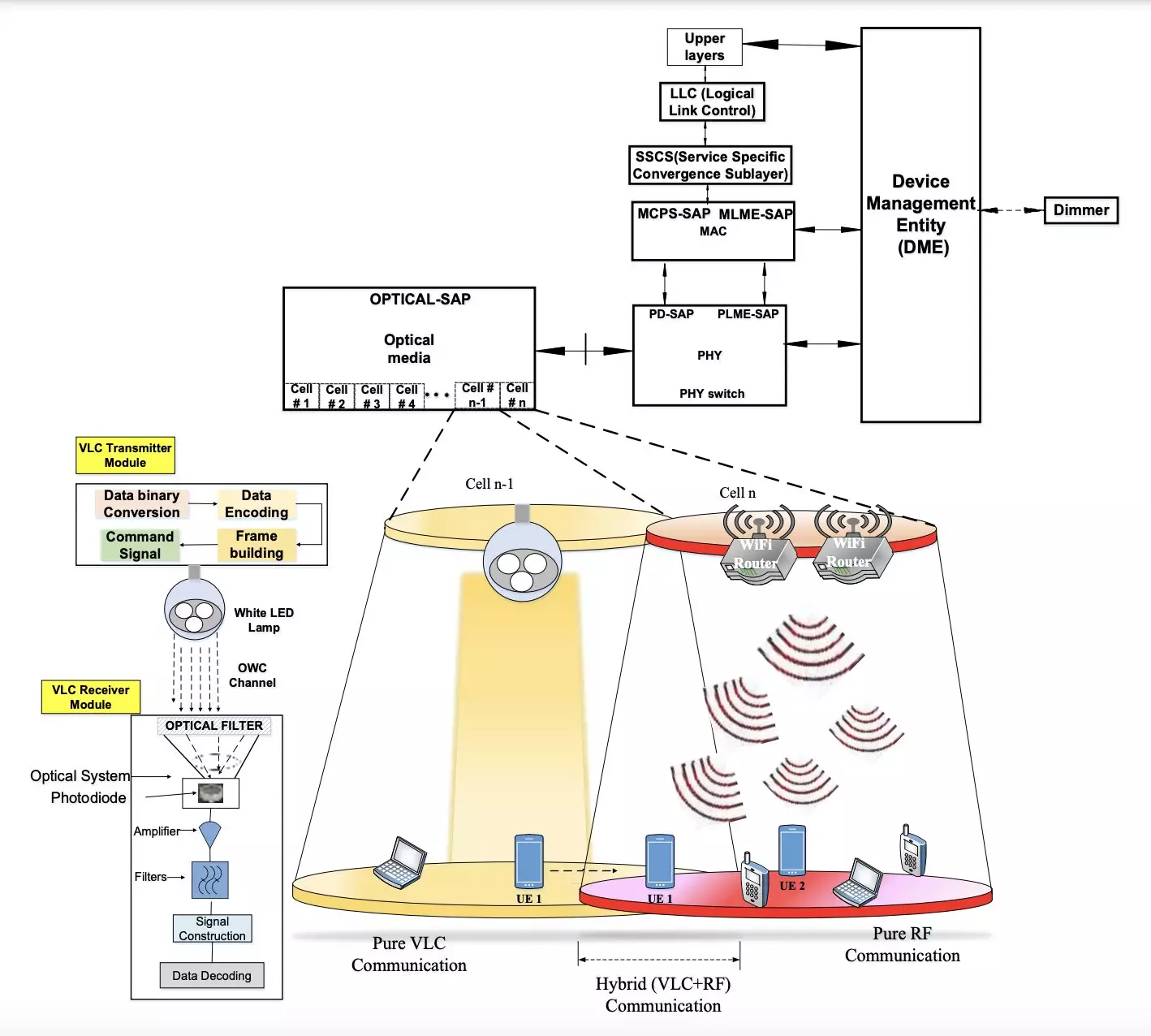
The proposed hybrid system by Kour, Jha, and Jain consists of a transmitter and a receiver module connected via a VLC channel. The transmitter utilizes LED-produced light to transmit binary data, while the receiver, equipped with a photosensitive device, extracts the information from the transmitted light. By implementing modulation schemes to ensure a continuous data stream and constant power consumption, the team aims to achieve reliable communication with minimal energy consumption.
Through various simulation platforms like Python, Scilab, and MathWorks, the researchers conducted a comparative analysis of RF communication, hybrid (RF+ VLC), and pure VLC systems. Their evaluation revealed that the proposed hybrid system not only enables stable communication in indoor environments but also significantly reduces energy consumption. The system’s high energy efficiency results in lower Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), decreased incident and absorbed power density, and improved battery life for mobile devices.
The innovative approach taken by Kour, Jha, and Jain in developing an energy-efficient wireless communication system holds great promise for the future. By merging VLC with RF communication, the hybrid system may pave the way for more sustainable and reliable wireless networks. As the team continues to refine their solution and conduct further studies, the potential impact on reducing power consumption and electromagnetic radiation in wireless communications could be substantial.
The research conducted by the team of researchers at CU, IIDM, and CU J&K highlights the importance of developing energy-efficient wireless communication technologies. Through their hybrid approach combining VLC and RF communication, they have demonstrated the potential for significant energy savings and improved communication reliability. As we look towards a future where sustainability is key, innovations in wireless communication technology will play a crucial role in minimizing our carbon footprint and ensuring a greener tomorrow.

Leave a Reply