Greenhouse gases play a significant role in global warming potential, with different gases having varying impacts on the environment. While carbon dioxide (CO2) is often the most talked about greenhouse gas, others such as methane and perfluorocarbons (PFCs) also contribute to the warming of the planet. PFCs, in particular, have extremely high global warming potential and long lifespans in the atmosphere, making them a crucial focus for climate change mitigation efforts.
The Rapid Rise of PFC Emissions in China
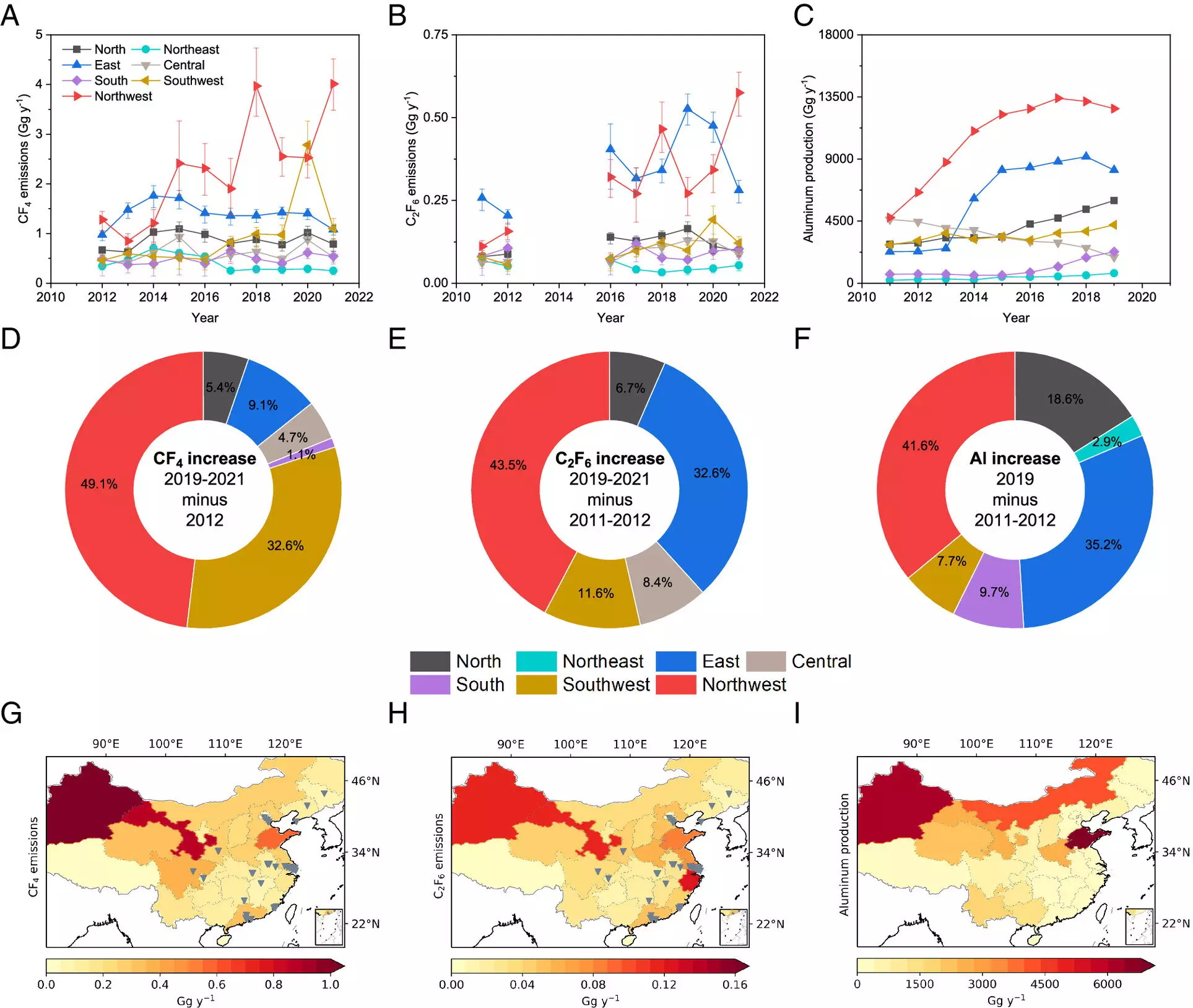
Recent studies have shown a rapid increase in PFC emissions in China over the past decade, specifically focusing on tetrafluoromethane (PFC-14), hexafluoroethane (PFC-116), and perfluorocyclobutane (PFC-318). These emissions have been driven primarily by the industrial sectors in China, with significant contributions from the aluminum and semiconductor industries. The rise in emissions of these gases in China has also had a global impact, contributing to the overall increase in PFC emissions worldwide.
The surge in PFC emissions in China poses a major challenge to global climate goals, including the targets set out in the Paris Agreement. With the goal of limiting the global average surface temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, reducing PFC emissions is crucial. The high global warming potential and long lifespans of PFCs make them a key focus for mitigating climate change and achieving these targets.
Both studies highlight the importance of pinpointing the sources of PFC emissions to develop targeted mitigation strategies. The less-populated western regions of China were found to have substantial emissions of PFC-14 and PFC-116, attributed to the aluminum industry. On the other hand, PFC-318 emissions primarily originated from the more economically developed eastern regions, particularly from factories producing polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Understanding the sources of these emissions is crucial in developing effective strategies to reduce PFC emissions.
Phasing out emissions of PFCs, as early as possible, is vital for achieving global climate mitigation targets. This can be achieved through recycling programs and targeted technological improvements in industries producing these gases. Identifying the actual source industries and understanding the reasons for these emissions is essential in implementing region- or industry-specific mitigation measures to reduce PFC emissions.
The rapid rise in PFC emissions in China poses a significant threat to global climate goals and the overall effort to combat climate change. As a major contributor to the increase in global PFC emissions, China must take immediate action to reduce these emissions and curb their impact on the environment. By understanding the sources of PFC emissions and implementing targeted mitigation strategies, China can play a significant role in mitigating the effects of these potent greenhouse gases on the planet.

Leave a Reply