A recent study published in Science Advances sheds light on the connection between mean annual temperatures (MAT) and phosphorus release in soils. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), highlights the importance of climate in influencing phosphorus weathering.
The study reveals that higher temperatures lead to enhanced phosphorus release from soils. This phenomenon, known as P weathering, has significant implications for the global cycling of key elements and the Earth’s biosphere. The data compiled by the researchers indicate that temperature plays a crucial role in regulating phosphorus mobility, with reduced P retention observed in warmer climates.
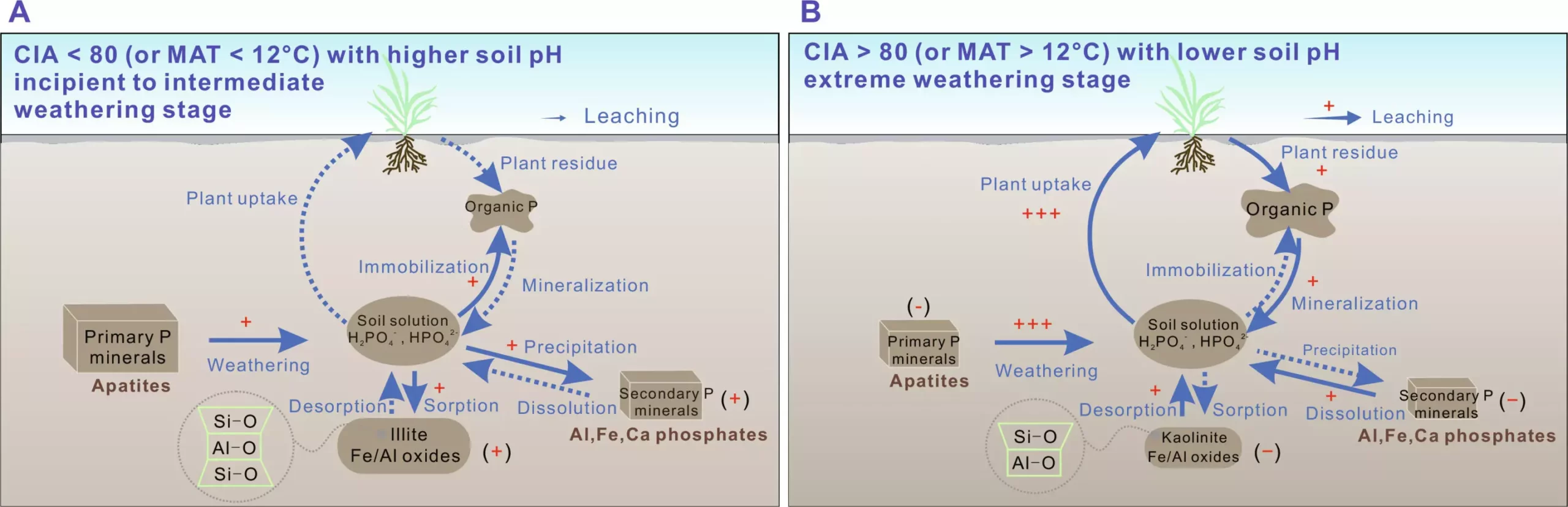
In environments with high weathering intensity, characterized by the leaching of key cations from fresh regolith, lower soil pH promotes the removal of primary apatite and the dissolution of phosphates. Additionally, a higher kaolinite/illite ratio in such environments results in a decreased P adsorption capacity within clay minerals. These findings underscore the complex interplay between climate, soil composition, and phosphorus dynamics.
The researchers also developed a model to calculate the relationship between modern global MAT and P weathering flux. The results indicate a rapid increase in phosphorus weathering flux within a specific temperature range. This has significant implications for nutrient supply, primary productivity, and the Earth’s natural thermostat. Furthermore, the study suggests that enhanced phosphorus release in warm climates could have played a role in past climate events, including oceanic anoxia.
One of the key findings of the study is the potential threat posed by anthropogenic climate change. The researchers warn that the acceleration of phosphorus loss from soils due to human activities could have detrimental effects on agricultural production, terrestrial and marine ecosystems, and marine redox landscapes. This highlights the urgent need to address the impact of climate change on phosphorus dynamics and ecosystem health.
The study emphasizes the intricate relationship between climate change and phosphorus release in soils. By understanding the mechanisms driving phosphorus weathering, researchers can better predict and mitigate the impacts of climate change on essential nutrient cycles and ecosystem functioning.

Leave a Reply